Notes For All Chapters Maths Class 6
Introduction to Understanding Elementary Shapes
There are so many shapes around us made up of lines and curves like line segments, angles, triangles, polygons and circles etc. These shapes are of different sizes and measures.
Measuring Line Segments
A line segment is a fixed part of the line, so it must have some length. We can compare any line segment on the basis of their length.
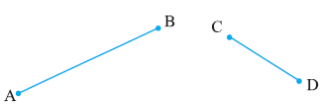
1. Comparison by Observation
We can tell which line segment is greater than other just by observing the two line segments but it is not sure.
Here we can clearly say that AB > CD but sometimes it is difficult to tell which one is greater.
2. Comparison by Tracing
In this method we have to trace one line on paper then put the traced line segment on the other line to check which one is greater.
But this is a difficult method because every time to measure the different size of line segments we have to make a separate line segment.
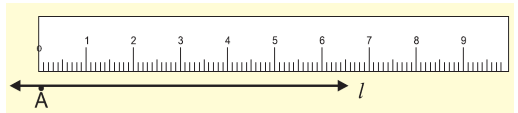
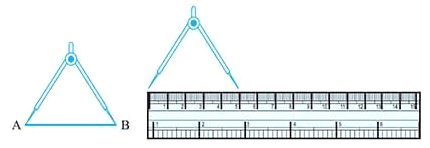
3. Comparison using Ruler and a Divider
We can use a ruler to measure the length of a line segment.
Put the zero mark at point A and then move toward l to measure the length of the line segment, but it may have some errors on the basis of the thickness of the ruler.
This could be made accurate by using a Divider.
(a) Put the one end of the divider on point A and open it to put another end on point B.
(b) Now pick up the divider without disturbing the opening and place it on the ruler so that one end lies on “0”.
(c) Read the marking on the other end and we can compare the two line.
Angles – “Right” and “Straight”
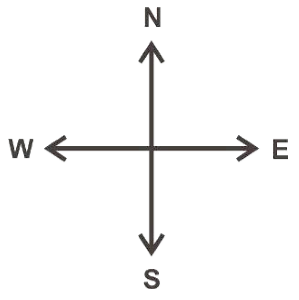
We can understand the concept of right and straight angles by directions.
There are four directions-North, South, East and West.
When we move from North to East then it forms an angle of 90° which is called Right Angle.
When we move from North to South then it forms an angle of 180° which is called Straight Angle.
When we move four right angles in the same direction then we reach to the same position again i.e. if we make a clockwise turn from North to reach to North again then it forms an angle of 360° which is called a Complete Angle. This is called one revolution.
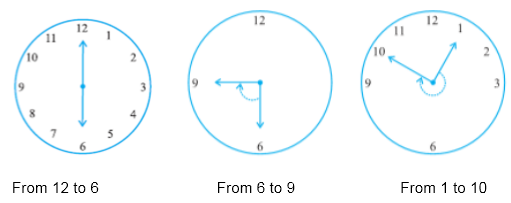
In a clock, there are two hands i.e. minute hand and hour hand, which moves clockwise in every minute. When the clock hand moves from one position to another then turns through an angle.
When a hand starts from 12 and reaches to 12 again then it is said to be completed a revolution.
Acute, Obtuse and Reflex Angles
There are so many other types of angles which are not right or straight angles.
| Angles | Meaning | Image |
| Acute Angle | An angle less than the right angle is called Acute angle. |  |
| Obtuse Angle | An angle greater than a right angle and less than straight angle is called Obtuse angle. |  |
| Reflex Angle | Angle greater than the straight angle is called Reflex angle. |  |
Measuring Angles
By observing an angle we can only get the type of angle but to compare it properly we need to measure it.
An angle is measured in the “degree”. One complete revolution is divided into 360 equal parts so each part is one degree. We write it as 360° and read as “three hundred sixty degrees”.
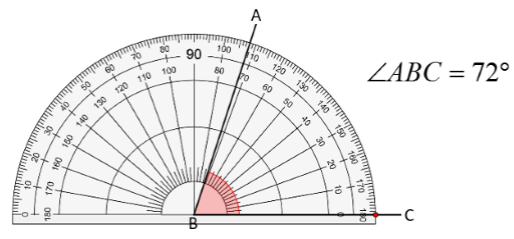
We can measure the angle using a ready to use device called Protractor.
It has a curved edge which is divided into 180 equal parts. It starts from 0° to 180° from right to left and vice versa.
To measure an angle using protractor-
(a) Place the protractor on the angle in such a way that the midpoint of protractor comes on the vertex B of the angle.
(b) Adjust it so that line BC comes on the straight line of the protractor.
(c) Read the scale which starts from 0° coinciding with the line BC.
(d) The point where the line AB comes on the protractor is the degree measure of the angle.
Hence, ∠ABC = 72°
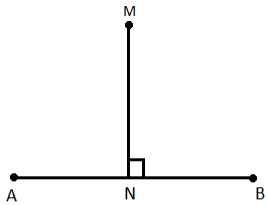
Perpendicular Lines
If two lines intersect with each other and form an angle of 90° then they must be perpendicular to each other.
Here AB and MN are intersecting at point N and form a right angle. We will write it as
AB ⊥ MN or MN ⊥ AB
Reads as AB is perpendicular to MN or MN is perpendicular to AB.
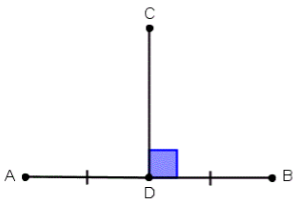
Perpendicular Bisector
If a perpendicular divides another line into two equal parts then it is said to be a perpendicular bisector of that line.
Here, CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB as it divides AB into two equal parts i.e. AD = DB.
Classification of Triangles
Triangle is a polygon with three sides. It is the polygon with the least number of sides. Every triangle is of different size and shape. We classify them on the basis of their sides and angles.
1. Classification on the basis of sides
| Triangle | Meaning | Image |
| Scalene | If all the sides are different then it is called scalene triangle. | 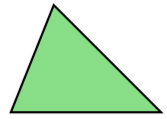 |
| Isosceles | If two sides are equal then it is called isosceles triangle. | 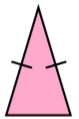 |
| Equilateral | If all the sides are equal then it is called equilateral triangle. | 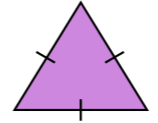 |
2. Classification on the basis of Angles
| Triangle | Meaning | Image |
| Acute Angled Triangle | If all the angles are less than 90° then this is called the acute-angled triangle. | 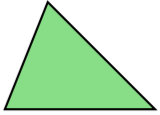 |
| Right Angled Triangle | If one of the angles is 90°then it is called the right-angled triangle. | 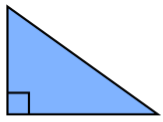 |
| Obtuse-angled Ariangle | If one of the angles of the triangle is obtuse angle then it is called Obtuse angled triangle. | 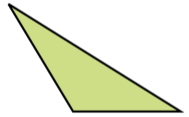 |
Quadrilaterals
A polygon with four sides is called Quadrilateral.
| S.No. | Name | Properties | Image |
| 1. | Rectangle |
|  |
| 2. | Square |
| 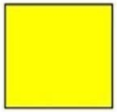 |
| 3. | Parallelogram |
|  |
| 4. | Rhombus |
| 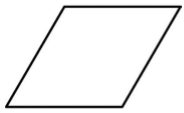 |
| 5. | Trapezium |
|  |
Polygons
Any closed figure made up of three or more line segments is called Polygon.
We can classify the polygons on the basis of their sides and vertices –
| Number of sides | Name of Polygon | Figure |
| 3 | Triangle |  |
| 4 | Quadrilateral |  |
| 5 | Pentagon |  |
| 6 | Hexagon |  |
| 7 | Heptagon |  |
| 8 | Octagon |  |
| 9 | Nonagon | 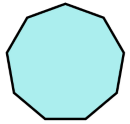 |
| 10 | Decagon | 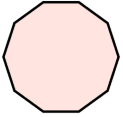 |
| n | n-gon |
Three-dimensional Shapes
The solid shapes having three dimensions are called 3D shapes.
Some of the 3D shapes around us
| Cone |  | ice-cream cone |
| Cube |  | Block |
| Cuboid |  | Match-box |
| Cylinder | Glass | |
| Sphere |  | Ball |
| Pyramid |  | Rubrics in a pyramid shape |
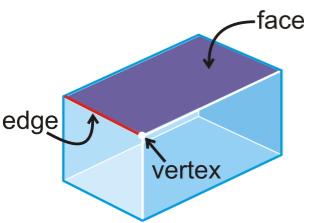
Faces, Edges and Vertices
All the flat surfaces of the solid shape are called the Faces of that figure.
The line segment where the two faces meet with each other is called Edge.
The point where the two edges meet with each other is called Vertex.
No. of Faces, Edges and Vertices in some common 3- D shapes
| S.No. | 3 – D shape | Figure | Faces | Edges | Vertices |
| 1. | Cube |  | 6 | 12 | 8 |
| 2. | Cuboid |  | 6 | 12 | 8 |
| 3. | Cone |  | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 4. | Sphere |  | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 5. | Cylinder |  | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| 6. | Square based Pyramid |  | 6 | 8 | 5 |
| 7. | Triangular Prism | 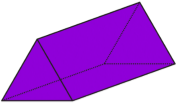 | 5 | 9 | 6 |
| 8. | Rectangular Prism | 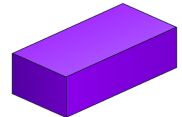 | 6 | 12 | 8 |


Leave a Reply