Notes For All Chapters Maths Class 8
Curve: A figure formed on a plane surface by joining a number of points without lifting a pencil is called a curve.
Open Curve: A curve which does not end at the same starting point or which does not cut itself is called an open curve.
Closed Curve: A curve which cut itself or which starts and ends at the same point is called a closed curve.
Simple Closed Curve: A closed curve called a simple closed curve which does not intersect itself.
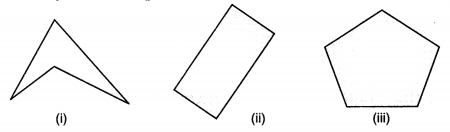
Polygon: A polygon is a closed figure bounded by three or more line segments such that each line segment intersects exactly two other points (vertices) as shown in the following figures.
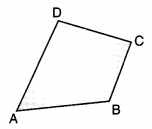
Quadrilateral: A simple closed figure bounded by four line segments is called a quadrilateral, it has four sides i.e., AB, BC, CD and AD and four vertices as A, B, C and D and the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
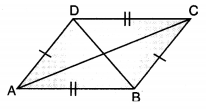
Parallelogram: A quadrilateral in which opposite sides are parallel and equal is called parallelogram; written as || gm. and the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Properties:
- Opposite sides are equal and parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Diagonals bisect each other.
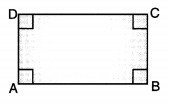
Rectangle: A parallelogram each of whose angle is 90° and diagonals are equal, is called a rectangle.
Properties:
- Opposite sides are equal and parallel.
- Each angle is a right angle.
- Diagonals are equal.
- Diagonals bisect each other.
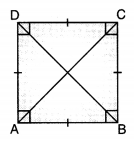
Square: A quadrilateral in which all sides and angles are equal, is called a square.
Properties:
- All the sides are equal and parallel.
- Each angle is a right angle.
- Diagonals are equal.
- Diagonals bisect each other at a right angle.
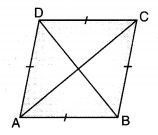
Rhombus: A parallelogram having all its sides equal, is called a rhombus.
Properties:
- All the side are equal.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Diagonals bisect each other at a right angle.
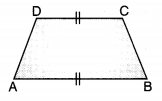
Trapezium: A quadrilateral in which two opposite sides are parallel and the other two opposite sides are non-parallel, is called a trapezium.
If two non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal, then it is called an isosceles trapezium.
The line segment joining the mid-points of non-parallel sides of a trapezium is called it’s median.
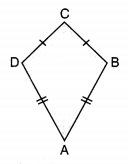
Kite: A quadrilateral in which two pairs of adjacent sides are equal, is called a kite.
Properties:
Diagonals bisect each other at the right angle.
In the figure, m ∠B = m ∠D, but m∠A ≠ m ∠C
Paper is a very common example of a plane surface. The curve obtained by joining a number of points consecutively without lifting the pencil from the paper is called a plane curve. A circle is a very common example of a plane curve.
A polygon is a simple closed curve formed of only line segments. A triangle is a very common example of a polygon.
Diagonals
The line-segment joining any two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon is called its diagonal.
Convex and Concave Polygons
A polygon is said to be convex if it has no portion of its diagonals in its exterior otherwise it is said to be a concave polygon.
Regular and Irregular Polygons
A polygon which is both ‘equiangular’ (has all angles of equal measure) and ‘equilateral’ (has all sides of equal measure) is called a regular polygon, for example, a square, an equilateral triangle.
A polygon which is equiangular but not equilateral is called an irregular polygon. For example; a rectangle.
The sum of the measures of the three angles of a triangle is 180°.
The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon is 360°.
Kinds of Quadrilaterals
The important types of quadrilaterals are as follows:
- Trapezium
- Kite
- Parallelogram
- Rhombus
- Rectangle
- Square.
Trapezium
A quadrilateral which has only one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezium.
Kite
A quadrilateral, which has exactly two pairs of equal consecutive sides, is called a kite.
Parallelogram
A quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel is called a parallelogram.
Elements of a Parallelogram
The elements of a parallelogram are as follows:
- two pairs of opposite sides
- four pairs of adjacent sides
- two pairs of opposite equal angles
- four pairs of adjacent angles.
The opposite sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
The opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equal measure.
The adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary.
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other at their point of intersection.
Rhombus
A quadrilateral whose all the four sides are of equal length is called a rhombus.
The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
Rectangle
A rectangle is a parallelogram with equal angles.
The diagonals of a rectangle are of equal length.
Square
A square is a rectangle whose all the four sides are equal.
The diagonals of a square are perpendicular bisectors of each other.

Nice Note