Notes For All Chapters Maths Class 8
To construct a quadrilateral uniquely, it is necessary to have the knowledge of at least five of its parts.
Five necessary parts to construct a quadrilateral may be:
- four sides and diagonal
- Three sides and two diagonals
- Four sides and an angle
- Three sides and two included angles
- Two adjacent sides and three angles
To construct a rhombus:
- Draw a diagonal of a given length and draw perpendicular bisector of this diagonal base.
- Take half of the given measurement of second diagonal and cut off arcs on either side of the perpendicular bisector. It will give two points of a rhombus.
- Join these points with the points on the first diagonal. It will give the required rhombus.
Before constructing a quadrilateral, one must draw a rough sketch of given measurements.
Trapezium, rhombus, and square are different forms of a parallelogram.
A rhombus can be a parallelogram, but a parallelogram cannot be a rhombus.
A square and a rhombus both have equal sides and a square can be rhombus but a rhombus cannot be a square.
We have learned the procedure of drawing triangles in the preceding class. We know that three measurements (of sides and angles) are required to draw a unique triangle. Here, we shall investigate whether four measurements are sufficient to draw a quadrilateral or not.
Constructing A Quadrilateral
We shall learn how to draw a unique quadrilateral when the following measurements are given:
- four sides and one diagonal
- two diagonals and three sides
- two adjacent sides and three angles
- three sides and two included angles
- other special properties.
When the Lengths of Four Sides and a Diagonal are given
In this case we divide the quadrilateral into two triangles which can be easily drawn with the help of the given measurements.
Suppose that we are to construct the quadrilateral ABCD. Then two cases arise:
- Diagonal AC is given: Here we divide the quadrilateral ABCD into two triangles ABC and ADC which can be easily drawn.
- Diagonal BD is given: Here we divide the quadrilateral ABCD into two triangles ABD and BCD which can be easily drawn.
When Two Diagonals and Three Sides are given
In this case, we draw any one of the two diagonals. It determines two vertices of the quadrilateral. Then taking two suitable sides of the three sides, we locate the third vertex of the quadrilateral. Finally using the second diagonal and the remaining side, we locate the fourth vertex of the quadrilateral.
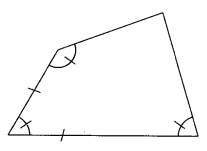
When Two Adjacent Sides and Three Angles are Known
We know that the sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360°. Since the three angles are given, therefore, if need be, the measure of the fourth angle can be readily obtained.
Thus, the angle between two adjacent sides is known if it is not even already given.
To construct the quadrilateral, we first draw two adjacent sides with the included angle between them. Then, at the other extremities of the adjacent sides, we draw rays at the given angles so as to intersect at a vertex (fourth) of the quadrilateral.
Thus the quadrilateral can be drawn completely.
When Three Sides and Two included Angles are Given
We specifically note the three sides and the two included angles. First, we draw the common side of the two angles. At its extremities, we draw the other sides of the given angles with their given measures. In the last, we join the extremities of the other two sides. Thus, we can draw the quadrilateral completely.
Some Special Cases
There are certain specific quadrilaterals which can be constructed with less number (<5) of available measurements.

Leave a Reply