Notes For All Chapters Maths Class 8
Square Number:
The square of a number is the product of the number with the number itself Thus, square of x = (x × x), denoted by x2.
A natural number n is a perfect square, if n = m2 for some natural number m.{1 = 1 × 1 = 12, 4 = 2 × 2 = 22}
Square Root:
Square root is the inverse operation of square, i.e., positive square root of a number is denoted by the symbol √
For example, 32 = 9 gives √9 = 3 or (32)1/2 = 3.
For positive numbers a and b, we have
Properties of the Square Number:
A number ending in 2, 3, 7 or 8 is never a perfect square.
A number ending in an odd number of zeros is never a perfect square.
The square of an even number is even.
The square of an odd number is odd.
The square of a proper fraction is smaller than the fraction.
For every natural number n, we have {(n + 1)2 – n2} = {(n + 1) + n}.
Sum of first n odd natural numbers = n2.
If m, n, p are natural numbers such that (m2 + n2) = p2, then (m, n, p) is called a Pythagorean triplet.
For every natural number m > 1, (2m, m2 – 1, m2 + 1) is a Pythagorean triplet.
There are 2n non-perfect square numbers between the squares of the number n and (n + 1).
The numbers which can be expressed as the product of the number with itself are called square numbers or perfect squares.
For example, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, ….
If a natural number m can be expressed as n2, where n is also a natural number, then, m is called a square number.
Some More Interesting Patterns
A triangular number is one whose dot patterns can be arranged as triangles. If we combine two consecutive triangular numbers, we get a square number.
There are 2n non-perfect square numbers between the squares of the numbers n and (n + 1) which is 1 less than the difference of two squares.
Sum of first n odd natural numbers is n2.
If a natural number cannot be expressed as a sum of successive odd natural number starting with 1, then it is not a perfect square. In other words, if a natural number is a square number, then it is necessarily the sum of successive odd numbers starting with 1. This result can be used to decide whether a given natural number is a perfect square or not.
We can express the square of any odd number as the sum of two consecutive positive integers.
If (n + 1) and (n – 1) are two consecutive even or odd natural numbers, then (n + 1) × (n – 1) = n2 – 1.
Finding the Square of a Number
See 232 = (20 + 3)2 = (20 + 3) (20 + 3)
= 20 (20 + 3) + 3 (20 + 3)
= 202 + 20 × 3 + 3 × 20 + 32
= 400 + 60 + 60 + 9
= 529
Other Patterns in Squares
Let a 5 be a number with unit digit 5. Then, (a5)2 = a (a + 1) hundred +25
Pythagorean Triplets Important Points
If a, b and c are three numbers such that any one of the following three relations holds:
(i) a2 + b2 = c2
(ii) b2 + c2 = a2
(iii) c2 + a2 = b2
then the numbers a, b, c are said to form a Pythagorean triplet.
For example: 3, 4, 5 is a Pythagorean triplet because 32 + 42 = 9 + 16 = 25 = 52.
we can find more such triplets.
For example: 8, 15, 17; 12, 9, 15; 12, 35, 37 etc.
Square Roots
The square root of a number ‘a’ is that number which when multiplied by itself gives that number ‘a’ as product.
Thus, if b is the square root of a;
then b × b = a or b2 = a
Symbolically, we write b = √a
Note: b= √a ⇔ b2 = a
i.e., b is the square root of an if and only if a is the square of b.
Finding Square Roots
To find, a number whose square is known is known as finding the square root.
Finding the square root is the inverse (opposite) operation of squaring.
There are two integral square roots of a perfect square number.
For example: 4 = (2)2 = (-2)2
√4 = 2 and 2 both. Here, we shall take up only positive square root of a natural number.
Thus, √4 = 2 (not -2)
The positive square root of a number is denoted by the symbol √.
For example, 32 = 9 ⇒ √9 = 3
Finding Square Root Through Repeated Subtraction
We subtract successive odd number starting from 1 from the given square number till we get zero. The number of times, we have to make subtractions, is called the square root of the given square number.
Finding Square Root Through Prime Factorisation
We find the prime factors of the given perfect square and arrange in pairs. Then, we choose one factor from each pair and multiply together. The product thus obtained gives the required square root.
Note: A square number has complete pairs of its prime factors.
Finding Square Root By Division Method
Steps
(i) Obtain the number whose square root is to be found. Place a bar over every pair of digits starting from the digit at one’s place. If the number of digits in it is odd, then the left-most single digit too will have a bar. Each pair and the left-most single digit (if any) is called a period.
(ii) Think of the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the number under the extreme left bar. Take this number as the divisor and the quotient with the number under the extreme left bar as the dividend. Divide and get the remainder.
(iii) Bring down the number under the next bar to the right of the remainder. This becomes the new dividend.
(iv) Double the divisor and enter it with a blank on its right.
(v) Guess a largest possible digit to fill the blank which will also become the new digit in the quotient, such that when the new divisor is multiplied to the new quotient, the product is less than or equal to the new dividend obtained in step (iii).
(vi) Continue this process till the remainder is 0 and no digits are left in the given number. The quotient thus obtained is the required square root of the given number.
Square Roots of Decimals
Put bars on an integral part of the number in the usual manner. Place bars in the decimal part on every pair of digits beginning with the first decimal place. Proceed as usual to find the square root.
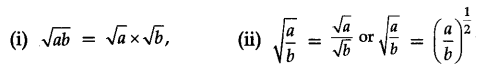
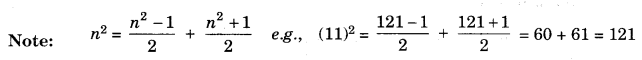

Very nice
Pls also arrange mock test and update sample paper btw best website
Best sellers
please convert the notes in pdf form