Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 8
Ex 13.1 Class 8 Maths Question 1.
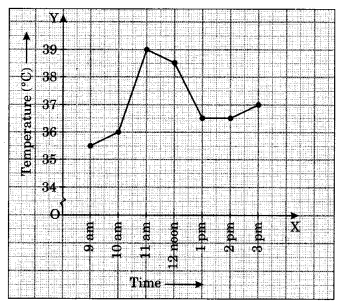
The following graph shows the temperature of a patient in a hospital, recorded every hour.
(a) What was the patient’s temperature at 1 pm?
(b) When was the patient’s temperature 38.5°C?
(c) The patient’s temperature was the same two times during the period given. What were the two times?
(d) What was the temperature at 1:30 pm? How did you arrive at your answer?
(e) During which periods did the patient’s temperature show an upward trend?
Solution:
(a) The patient’s temperature at 1 pm was 36.5°C
(b) The patient’s temperature was 38.5°C at 12:00 noon.
(c) The patients temperature was 36.5°C at 1 pm and 2 pm.
(d) The temperature at 1:30 pm was 36.5°C. We have taken the mid value of 1 pm. and 2 pm, i.e., 1:30 p.m and proceed perpendicularly upwards to meet the horizontal line showing 36.5°C.
(e) During 9 am to 10 am and 10 am to 11 am, the temperature showed upwards trend.
Ex 13.1 Class 8 Maths Question 2.
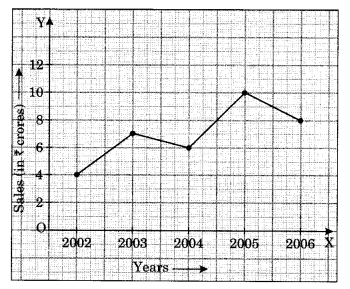
The following line graph shows the yearly sales figures for a manufacturing company.
(a) What were the sales in (i) 2002 (ii) 2006?
(b) What were the sales in (i) 2003 (ii) 2005?
(c) Compute the difference between the sales in 2002 and 2006.
(d) In which year was there the greatest difference between the sales as compared to its previous year?
Solution:
(a) The sales in the year 2002 was ₹ 4 crore and in the year 2006 was ₹ 8 crore.
(b) The sales in the year 2003 was ₹ 7 crore and in 2005 was ₹ 10 crore.
(c) Sales in 2002 = ₹ 4 crore
Sales in 2006 = ₹ 8 crores
Difference = ₹ (8 – 4) crore = ₹ 4 crore.
(d) The greatest difference between the sales was in the year 2005, as compared to previous year.
Ex 13.1 Class 8 Maths Question 3.
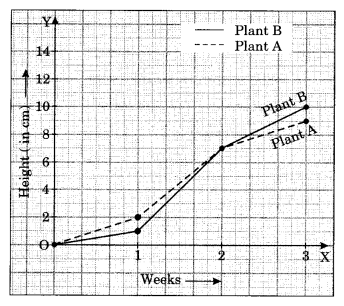
For an experiment in Botany, two different plants, plant A and plant B, were grown under similar laboratory conditions. Their heights were measured at the end of each week for 3 weeks. The results are shown by the following graph.
(a) How high was plant A after (i) 2 weeks (ii) 3 weeks
(b) How high was plant B after (i) 2 weeks (ii) 3 weeks
(c) How much did plant A grow during the 3rd week?
(d) How much did plant B grow from the end of the 2nd week to the end of the 3rd week?
(e) During which week did plant A grow most?
(f) During which week did plant B grow least?
(g) Were the two plants of the same height during any week shown here? Specify.
Solution:
(a) The height of plant A (i) after 2 weeks was 7 cm (ii) after 3 weeks was 9 cm.
(b) The height of plant B (i) after 2 weeks was 7 cm (ii) after 3 weeks was 10 cm.
(c) Plant A grew 7 cm to 9 cm i.e, 2 cm.
(d) Plant B grew 7 cm to 10 cm i.e., 3 cm.
(e) Plant A grew most in a 2nd week i.e., 5 cm.
(f) Plant B grew the least in a first week i.e., 1 cm.
(g) Yes, the two plants grew the same height at the end of 2nd week i.e., 7 cm.
Ex 13.1 Class 8 Maths Question 4.
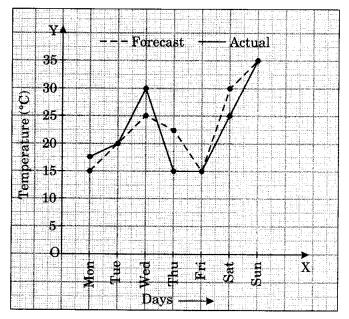
The following graph shows the temperature forecast and the actual temperature for each day of a week.
(a) On which days was the forecast temperature the same as the actual temperature?
(b) What was the maximum forecast temperature during the week?
(c) What was the minimum actual temperature during the week?
(d) On which day did the actual temperature differ the most from the forecast temperature?
Solution:
(a) On Tuesday, Friday and Sunday, the forecast temperature was the same as the actual temperature i.e., 20°C, 15°C and 35°C respectively.
(b) The forecast maximum temperature during the week was 35°C
(c) The minimum actual temperature during the week was 17.5°C
(d) On Thursday, the actual temperature differed the most from the forecast temperature
i.e., 22.5°C – 15°C = 7.5°C.
Ex 13.1 Class 8 Maths Question 5.
Use the tables below to draw linear graphs.
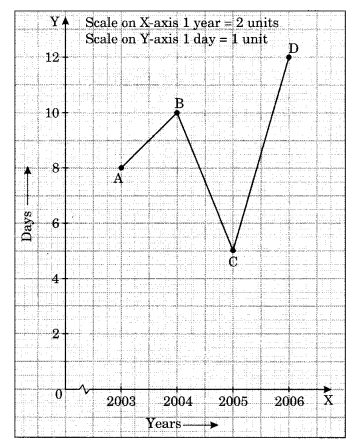
(a) The number of days a hillside city recovered show in different years.
| Year | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
| Days | 8 | 10 | 5 | 12 |
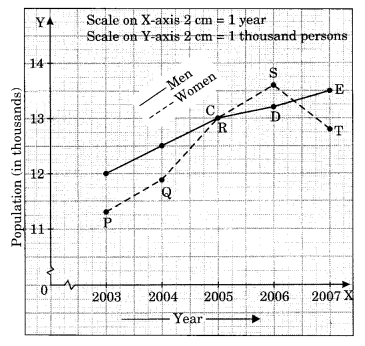
(b) Population (in thousands) of men and women in a village is different years.
| Year | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 |
| Number of men | 12 | 12.5 | 13 | 13.2 | 13.5 |
| Number of women | 11.3 | 11.9 | 13 | 13.6 | 12.8 |
Solution:
Ex 13.1 Class 8 Maths Question 6.
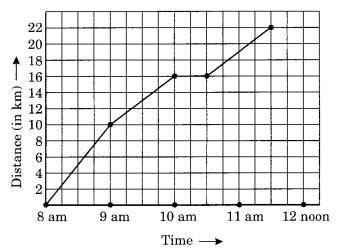
A courier-person cycle from a town to a neighbouring suburban area to deliver a parcel to the merchant. His distance from the town at different times is shown by the following graph.
(a) What is the scale taken for the time axis?
(b) How much time did the person take for travel?
(c) How far is the place of the merchant from the town?
(d) Did the person stop on his way? Explain?
(e) During which period did he ride fastest?
Solution:
(a) Scale taken on time-axis i.e., the x-axis is 4 units = 1 hour
(b) Total time taken by the person for the total journey is 3 hours 30 minutes.
(c) The place of the merchant is at a distant of 22 km from the town.
(d) Yes, this is indicated by the horizontal part of the graph clearly the person stopped from 10 am to 10:30 am.
(e) He rode fastest between 8 am and 9 am.
Ex 13.1 Class 8 Maths Question 7.
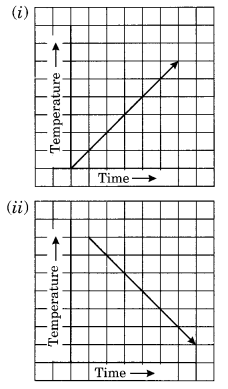
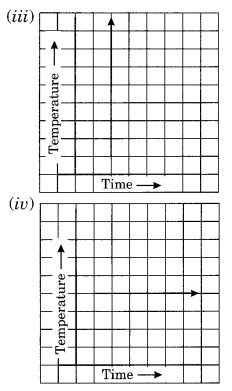
Can there be a time-temperature graph as follows? Justify your answer.
Solution:
(i) It represents a time-temperature graph where temperature increases as the time increase.
(ii) It shows a time-temperature graph where temperature decreases as the time increases.
(iii) It does not represent a time-temperature graph. Here the temperature is increasing at the constant time which is not possible.
(iv) It represents a time-temperature graph where the temperature remains constant when the time is increasing.

Good Website
Solution of chapter 13 exercise 13.2 question number 1. (a)