Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 8
Ex 13.2 Class 8 Maths Question 1.
Draw the graphs for the following tables of values, with suitable scales on the axes.
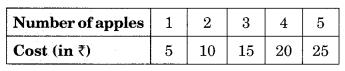
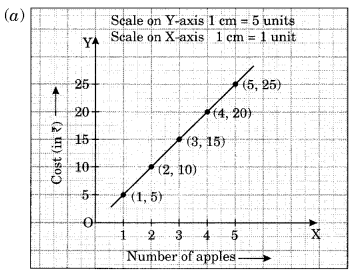
(a) Cost of apples
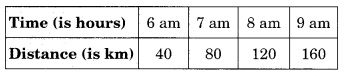
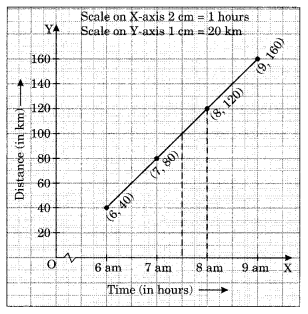
(b) Distance travelled by car.
(i) How much distance did the car cover during the period 7:30 am to 8 am?
(ii) What was the time when the car had covered a distance of 100 km since its start?
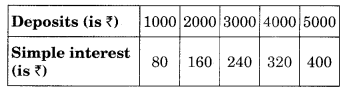
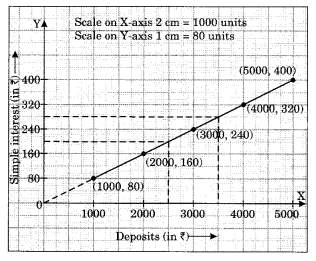
(c) Interest on deposits for a year.
(i) Does the graph pass through the origin?
(ii) Use the graph to find the interest on ? 2500 for a year.
(iii) To get an interest of t 280 per year, how much money should be deposited?
Solution:
(b) (i) The distance covered by the car during the period 7:30 am to 8 am is (120 km – 100 km) = 20 km.
(ii) At 7:30 am, the car had covered a distance of 100 km.
(c) (i) Yes, the graph passes through the origin,
(ii The interest on ₹ 2500 is ₹ 200 for 1 year.
(iii) ₹ 3500 should be invested to earn the interest of ₹ 280.
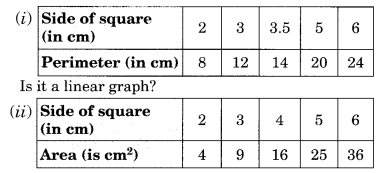
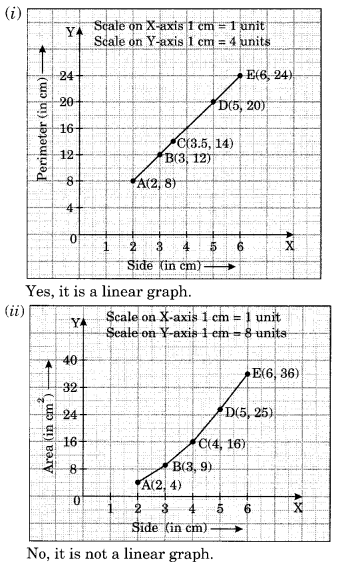
Ex 13.2 Class 8 Maths Question 2.
Draw the graph for the following:
Solution:

Thank you
Thank you mam for your help
No need that (A,B,C,D ) In each graph. Here after no problem 😊. Ok thank you for giving this answer
Yeahhh, thank you so much! I just came to this website to cross-check. 😏😁
It is very helpful I need chapter 13 before my annual exam. It is really helped me completing my work of maths so yea it was all good.. 😌💯
Thankyou for your answer it really helped me
Really very helpful.🥺🫡
Thank you so much. 🥰😘
Truly appriciatable.😊🤠
thnx
Good 👍👍👍👍😊😊 Work I give 5 Stars
Thank you for providing the answer! I truly appreciate it, thank you so much!
Thank you for you great answer 💗💗💗
👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍👍
Thank you for your answer 😊
Thank you 👍😊👍😊👍😊 👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍😊👍
Thankyou
Love you 🤟😘
Thank you for giving me answer 🙏☺️
It is very helpful…. Cuz I need ch 13 before my annual exam. It really helped me completing my work of maths ….. So yea it was all gud