Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 8
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 1.
Solution:
⇒ 30x – 12 = 20x + 15
⇒ 30x – 20x = 15 + 12 (Transposing 20x to LHS and 12 to RHS)
⇒ 10x = 27
⇒ x = 27/10
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 2.
Solution:
LCM of 2, 4 and 6 = 12
(Multiplying both sides by 12)
⇒ 6n – 9n + 10n = 252
⇒ 7n = 252
⇒ n = 252 ÷ 7
⇒ n = 36
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 3.
Solution:
⇒ -10x + 42 = 17 – 15x
⇒ -10x + 15x = 17 – 42 [Transposing 15x to LHS and 42 to RHS]
⇒ 5x = -25
⇒ x = -25 ÷ 5 [Transposing 5 to RHS]
⇒ x = -5
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 4.
Solution:
⇒ (x – 5) × 5 = (x – 3) × 3
⇒ 5x – 25 = 3x – 9 (Solving the brackets)
⇒ 5x – 3x = 25 – 9 (Transposing 3x to LHS and 25 to RHS)
⇒ 2x = 16
⇒ x = 16 ÷ 2 = 8 (Transposing 2 to RHS)
⇒ x = 8
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 5.
Solution:
⇒ (3t – 2) × 3 – (2t + 3) × 4 = 2 × 4 – 12t
⇒ 9t – 6 – 8t – 12 = 8 – 12t (Solving the brackets)
⇒ t – 18 = 8 – 12t
⇒ t + 12t = 8 + 18 (Transposing 12t to LHS and 18 to RHS)
⇒ 13t = 26
⇒ t = 2 (Transposing 13 to RHS)
Hence t = 2 is the required solution.
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 6.
Solution:
⇒ 6m – (m – 1) × 3 = 6 – (m – 2) × 2
⇒ 6m – 3m + 3 = 6 – 2m + 4 (Solving the brackets)
⇒ 3m + 3 = 10 – 2m
⇒ 3m + 2m = 10 – 3 (Transposing 2m to LHS and 3 to RHS)
⇒ 5m = 7
⇒ m = 7/5 (Transposing 5 to RHS)
Simplify and solve the following linear equations.
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 7.
3(t – 3) = 5(21 + 1)
Solution:
We have
3(t – 3) = 5(2t + 1)
⇒ 3t – 9 = 10t + 5 (Solving the brackets)
⇒ 3t – 10t = 9 + 5 (Transposing 10t to LHS and 9 to RHS)
⇒ -7t = 14
⇒ t = -2(Transposing -7 to RHS)
Hence, t = -2 is the required solution.
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 8.
15(y – 4) – 2(y – 9) + 5(y + 6) = 0
Solution:
We have 15(y – 4) – 2(y – 9) + 5(y + 6) = 0
⇒ 15y – 60 – 2y + 18 + 5y + 30 = 0 (Solving the brackets)
⇒ 8y – 12 = 0
⇒ 8y = 12 (Transposing 12 to RHS)
⇒ y = 2/3
Hence, y = 2/3 is the required solution.
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 9.
3(5z – 7) – 2(9z – 11) = 4(8z – 13) – 17
Solution:
We have
3(5z – 7) – 2(9z – 11) = 4(8z – 13) – 17
⇒ 15z – 21 – 18z + 22 = 32z – 52 – 17 (Solving the bracket)
⇒ -3z + 1 = 32z – 69
⇒ -3z – 32z = – 69 – 1 (Transposing 322 to LHS and 1 to RHS)
⇒ -35z = -70
⇒ z = 2
Hence, z = 2 is the required solution.
Ex 2.2 Class 8 Maths Question 10.
0.25(4f – 3) = 0.05(10f – 9)
Solution:
We have
0.25(4f – 3) = 0.05(10f – 9)
⇒ 0.25 × 4f – 3 × 0.25 = 0.05 × 10f – 9 × 0.05 (Solving the brackets)
⇒ 1.00f – 0.75 = 0.5f – 0.45
⇒ f – 0.5f = -0.45 + 0.75 (Transposing 0.5 to LHS and 0.75 to RHS)
⇒ 0.5f = 0.30
⇒ f = 0.6
Hence, f = 0.6 is the required solution.
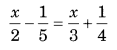
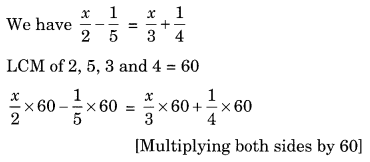
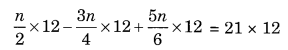
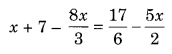
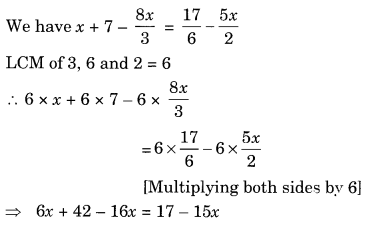
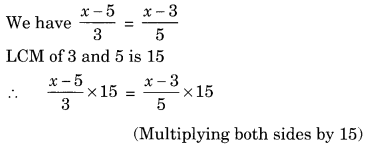
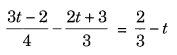
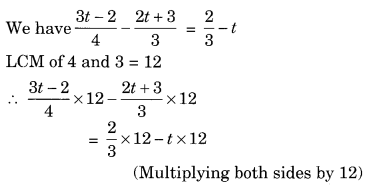
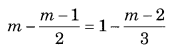
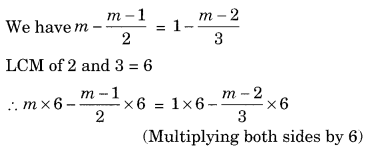

Leave a Reply