Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 8
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable Ex 2.4
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 1.
Amina thinks of a number and subtracts 5/2 from it. She multiplies the result by 8. The result now obtained is 3 times the same number she thought of. What is the number?
Solution:
Let the required number be x.
Condition I: x – 5/2
Condition II: 8 × (x –5/2)
Condition III: 8 × (x –5/2) = 3x
⇒ 8x – 5/2 × 8 = 3x (Solving the bracket)
⇒ 8x – 20 = 3x
⇒ 8x – 3x = 20 (Transposing 3x to LHS and 20 to RHS)
⇒ 5x = 20
⇒ x = 20 ÷ 5 = 4 (Transposing 5 to RHS)
Thus, x = 4 is the required number.
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 2.
A positive number is 5 times another number. If 21 is added to both the numbers, then one of the new numbers becomes twice the other number. What are the numbers?
Solution:
Let the positive number be x.
Other number = 5x
Condition I: x + 21 and 5x + 21
Condition II: 5x + 21 = 2 (x + 21)
⇒ 5x + 21 = 2x + 42 (Solving the bracket)
⇒ 5x – 2x = 42 – 21 (Transposing 2x to LHS and 21 to RHS)
⇒ 3x = 21
⇒ x = 21 ÷ 3 = 7 (Transposing 3 to RHS)
Thus, the required numbers are 7 and 7 × 5 = 35.
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 3.
Sum of the digits of a two digit number is 9. When we interchange the digits, it is found that the resulting new number is greater than the original number by 27. What is the two-digit number?
Solution:
Let unit place digit be x.
Ten’s place digit = 9 – x
Original number = x + 10(9 – x)
Condition I: 10x + (9 – x) (Interchanging the digits)
Condition II: New number = original number + 27
⇒ 10x + (9 – x) = x + 10(9 – x) + 27
⇒ 10x + 9 – x = x + 90 – 10x + 27 (solving the brackets)
⇒ 9x + 9 = -9x + 117 (Transposing 9x to LHS and 9 to RHS)
⇒ 9x + 9x = 117 – 9
⇒ 18x = 108
⇒ x = 108 ÷ 18 (Transposing 18 to RHS)
⇒ x = 6
Unit place digit = 6
Ten’s place digit = 9 – 6 = 3
Thus, the required number = 6 + 3 × 10 = 6 + 30 = 36
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 4.
One of the two digits of a two digit number is three times the other digit. If you interchange the digits of this two-digit number and add the resulting number to the original number, you get 88. What is the original number?
Solution:
Let unit place digit be x.
Ten’s place digit = 3x
Original number = x + 3x × 10 = x + 30x = 31x
Condition I: 10x + 3x = 13x (interchanging the digits)
Condition II: New number + original number = 88
13x + 31x = 88
⇒ 44x = 88
⇒ x = 88 ÷ 44 (Transposing 44 to RHS)
⇒ x = 2
Thus, the original number = 31x = 31 × 2 = 62
Hence the required number = 62
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 5.
Shobo’s mother’s present age is six times Shobo’s present age. Shobo’s age five years from now will be one third of his mother’s present age. What are their present ages?
Solution:
Let Shobo’s present age be x years.
Shobo’s mother’s age = 6x years.
After 5 years Shobo’s age will be (x + 5) years.
As per the condition, we have
x + 5 =1/3 × 6x
⇒ x + 5 = 2x
⇒ 5 = 2x – x (Transposing x to RHS)
⇒ 5 = x
Hence Shobo’s present age = 5 years
and Shobo’s mother’s present age 6x = 6 × 5 = 30 years.
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 6.
There is a narrow rectangular plot, reserved for a school, in Mahuli village. The length and breadth of the plot are in the ratio 11 : 4. At the rate of ₹ 100 per metre, it will cost the village panchayat ₹ 75000 to fence the plot. What are the dimensions of the plot?
Solution:
Let the length and breadth of the plot be 11x m and 4x m respectively.
Fencing all around = perimeter of the rectangular plot
Perimeter of the plot = 75000/100 = 750 m
2(l + b) = 750
⇒ 2(11x + 4x) = 750
⇒ 2(15x) = 750
⇒ 30x = 750
⇒ x = 750 ÷ 30 = 25
length = 11 × 25 m = 275 m
and breadth = 4 × 25 m = 100 m
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 7.
Hasan buys two kinds of cloth materials for school uniforms, shirt material that costs him ₹ 50 per metre and trousers material that costs him ₹ 90 per metre. For every 3 metres of the shirt material, he buys 2 metres of the trouser material. He sells the materials at 12% and 10% profit respectively. His total sale is ₹ 36,600. How much trouser material did he buy?
Solution:
Ratio of shirt material bought to the trouser material bought = 3 : 2
Let the shirt material bought = 3x m
and trouser material bought = 2x m
Cost of shirt material = 50 × 3x = ₹ 150x
Cost of trouser material = 90 × 2x = ₹ 180x
As per the conditions, we have
168x + 198x = 36,600
⇒ 366x = 36,600
⇒ x = 36600 ÷ 366 = 100
Length of trouser material bought = 2 × 100 = 200 m.
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 8.
Half of a herd of deer are grazing in the field and three-fourths of the remaining are playing nearby. The rest 9 are drinking water from the pond. Find the number of deer in the herd.
Solution:
Let the number of deer be x.
As per the condition, we have
x/2 deer are grazing in the field.
⇒ 4x + 3x + 72 = 8x
⇒ 7x + 72 = 8x
⇒ 72 = 8x – 7x (Transposing 7x to RHS)
⇒ x = 12
Hence, the required number of deer = 72.
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 9.
A grandfather is ten times older than his granddaughter. He is also 54 years older than her. Find their present ages.
Solution:
Let the present age of granddaughter = x years.
the present age of grandfather = 10x years.
As per the conditions, we have
10x – x = 54
⇒ 9x = 54
⇒ x = 54 ÷ 9 = 6 [Transposing 9 to RHS]
Hence, the present age of the granddaughter = 6 years
and the present age of grandfather = 6 × 10 = 60 years.
Ex 2.4 Class 8 Maths Question 10.
Aman’s age is three times his son’s age. Ten years ago he was five times his son’s age. Find their present ages.
Solution:
Let the present age of the son be x years.
Present age of Aman = 3x years
10 years ago, the son’s age was = (x – 10) years
10 years ago, the father’s age was = (3x – 10) years
As per the conditions, we have
5(x – 10) = 3x – 10
⇒ 5x – 50 = 3x – 10
⇒ 5x – 3x = 50 – 10(Transposing 3x to LHS and 50 to RHS)
⇒ 2x = 40
⇒ x = 40 ÷ 2 = 20
Hence, the son’s age = 20 years.
and the age of Aman = 20 × 3 = 60 years.
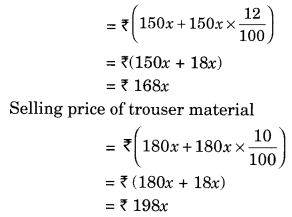


Leave a Reply