Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 8
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry Ex 4.5
Draw the following:
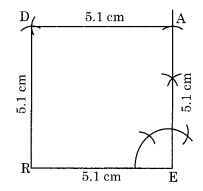
Ex 4.5 Class 8 Maths Question 1.
The square READ with RE = 5.1 cm.
Solution:
Construction:
Step I: Draw RE = 5.1 cm.
Step II: Draw an angle of 90° at E and cut EA = 5.1 cm.
Step III: Draw two arcs from A and R with radius 5.1 cm to cut each other at D.
Step IV: Join RD and AD.
Thus, READ is the required square.
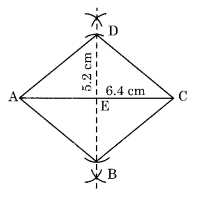
Ex 4.5 Class 8 Maths Question 2.
A rhombus whose diagonals are 5.2 cm and 6.4 cm long.
Solution:
Construction:
Step I: Draw AC = 6.4 cm.
Step II: Draw the right bisector of AC at E.
Step III: Draw two arcs with centre E and radius = 5.2/2 = 2.6 cm to cut the previous diagonal at B and D.
Step IV: Join AD, AB, BC and DC.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.
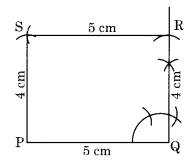
Ex 4.5 Class 8 Maths Question 3.
A rectangle with adjacent sides of lengths 5 cm and 4 cm.
Solution:
Construction:
Let the two adjacent sides of a rectangle PQRS be PQ = 5 cm and QR = 4 cm.
Step I: Draw PQ = 5 cm.
Step II: Draw an angle of 90° at Q and cut QR = 4 cm.
Step III: Draw an arc with centre R and radius 5 cm.
Step IV: Draw another arc with centre P and radius 4 cm to meet the previous arc at S.
Step V: Join RS and PS.
Thus, PQRS is the required rectangle.
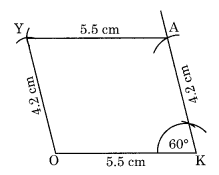
Ex 4.5 Class 8 Maths Question 4.
A parallelogram OKAY where OK = 5.5 cm and KA = 4.2 cm. Is it unique?
Solution:
Construction:
Step I: Draw OK = 5.5 cm.
Step II: Draw an angle of any measure (say 60°) at K and cut KA = 4.2 cm.
Step III: Draw an arc with centre A and radius of 5.5 cm.
Step IV: Draw another arc with centre O and radius 4.2 cm to cut the previous arc at Y.
Step V: Join AY and OY.
Thus, OKAY is the required parallelogram.
No, it is not a unique parallelogram. The angle at K can be of measure other than 60°.

Leave a Reply