Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 8
Ex 6.1 Class 8 Maths Question 1.
Which of the following numbers are not perfect cubes?
(i) 216
(ii) 128
(iii) 1000
(iv) 100
(v) 46656
Solution:
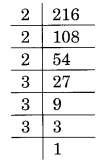
(i) Prime factorisation of 216 is:
216 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3
In the above factorisation, 2 and 3 have formed a group of three.
Thus, 216 is a perfect cube.
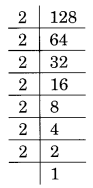
(ii) Prime factorisation of 128 is:
128 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
Here, 2 is left without making a group of three.
Thus 128 is not a perfect cube.
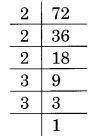
(iii) Prime factorisation of 1000, is:
1000 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × 5
Here, no number is left for making a group of three.
Thus, 1000 is a perfect cube.
(iv) Prime factorisation of 100, is:
100 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5
Here 2 and 5 have not formed a group of three.
Thus, 100 is not a perfect cube.
(v) Prime factorisation of 46656 is:
46656 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
Here 2 and 3 have formed the groups of three.
Thus, 46656 is a perfect cube.
Ex 6.1 Class 8 Maths Question 2.
Find the smallest number by which each of the following numbers must be multiplied to obtain a perfect cube.
(i) 243
(ii) 256
(iii) 72
(iv) 675
(v) 100
Solution:
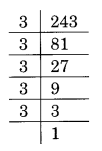
(i) Prime factorisation of 243, is:
243 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 3³ × 3 × 3
Here, number 3 is required to make 3 × 3 a group of three, i.e., 3 × 3 × 3
Thus, the required smallest number to be multiplied is 3.
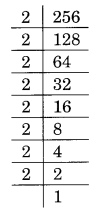
(ii) Prime factorisation of 256, is:
256 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 2³ × 2³ × 2 × 2
Here, a number 2 is needed to make 2 × 2 a group of three, i.e., 2 × 2 × 2
Thus, the required smallest number to be multiplied is 2.
(iii) Prime factorisation of 72, is:
72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 = 2³ × 3 × 3
Here, a number 3 is required to make 3 × 3 a group of three, i.e. 3 × 3 × 3
Thus, the required smallest number to be multiplied is 3.
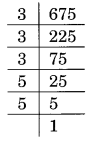
(iv) Prime factorisation of 675, is:
675 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 5 = 3³ × 5 × 5
Here, a number 5 is required to make 5 × 5 a group of three to make it a perfect cube, i.e. 5 × 5 × 5
Thus, the required smallest number is 5.
(v) Prime factorisation of 100, is:
100 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5
Here, number 2 and 5 are needed to multiplied 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 to make it a perfect cube, i.e., 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × 5
Thus, the required smallest number to be multiplied is 2 × 5 = 10.
Ex 6.1 Class 8 Maths Question 3.
Find the smallest number by which each of the following numbers must be divided to obtain a perfect cube.
(i) 81
(ii) 128
(iii) 135
(iv) 92
(v) 704
Solution:
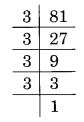
(i) Prime factorisation of 81, is:
81 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 3³ × 3
Here, a number 3 is the number by which 81 is divided to make it a perfect cube,
i.e., 81 ÷ 3 = 27 which is a perfect cube.
Thus, the required smallest number to be divided is 3.
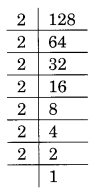
(ii) Prime factorisation of 128, is:
128 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 2³ × 2³ × 2
Here, a number 2 is the smallest number by which 128 is divided to make it a perfect cube,
i.e., 128 ÷ 2 = 64 which is a perfect cube.
Thus, 2 is the required smallest number.
(iii) Prime factorisation of 135 is:
135 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 = 3³ × 5
Here, 5 is the smallest number by which 135 is divided to make a perfect cube,
i.e., 135 ÷ 5 = 27 which is a perfect cube.
Thus, 5 is the required smallest number.
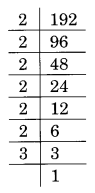
(iv) Prime factorisation of 192 is:
192 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 2³ × 2³ × 3
Here, 3 is the smallest number by which 192 is divided to make it a perfect cube,
i.e., 192 ÷ 3 = 64 which is a perfect cube.
Thus, 3 is the required smallest number.
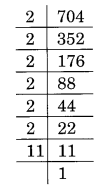
(v) Prime factorisation of 704 is:
704 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 11 = 2³ × 2³ × 11
Here, 11 is the smallest number by which 704 is divided to make it a perfect cube,
i.e., 704 ÷ 11 = 64 which is a perfect cube.
Thus, 11 is the required smallest number.
Ex 6.1 Class 8 Maths Question 4.
Parikshit makes a cuboid of plasticine of sides 5 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm. How many such cuboids will be needed to form a cube?
Solution:
The sides of the cuboid are given as 5 cm, 2 cm and 5 cm.
Volume of the cuboid = 5 cm × 2 cm × 5 cm = 50 cm³
For the prime factorisation of 50, we have
50 = 2 × 5 × 5
To make it a perfect cube, we must have
2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × 5
= 20 × (2 × 5 × 5)
= 20 × volume of the given cuboid
Thus, the required number of cuboids = 20.






It is too helpful for me when I will not attend the class
To complete homework ♥️🎉🥳
I think 💬💬 that it’s a good site for children ☺️☺️ . I also watch evidyarthi on YouTube..
Thankyou you ❤️❤️
Thank you evidyarthi 😊
Thankyou ✨💗 E vidyarthi
Copy assesment me 10 marks dilane ke liye✨🫶🏻🤍
Thanku you for this answer…
🥰👍
evidyarthi 🥰🥰
Thank you
E vidyarthi
🥰😚Thank you, so much for this🥰😊