Solutions For All Chapters Science Class 7
Q.1.Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called ___________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called _______.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of
another flower of the same kind is known as __________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as ____________ .
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of ________ and __________.
Ans.
(a) vegetative reproduction (b) unisexual flower (c) pollination (d) fertilization (e) wind, water
Q.2. Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Ans.
Different methods of asexual reproduction are:
(a) Binary Fission: This process takes place in unicellular organisms. Parent cell elongates and gets divided into two identical daughter cells. Each daughter cell grows into an independent adult.
(b) Endospore Formation: In this method the spore wall is formed around a bacterial cell to form an endospore. This endospore germinates to form an active bacterium under favourable conditions.
(c) Fragmentation: In this process, body of the organism breaks up into two parts. Then each part grows into a new filament thus forming two organisms from a single one.
(d) Spore Formation: The spores are tiny spherical unicellular structures protected by thick wall. The spores are stored in a hard outer covering and this is called sporangium. Under favourable conditions the hard cover breaks and spores spread for germination.
(e) Budding: In yeast, new organisms are produced by the bud formation from the parent organism. After growing to full size, the bud gets detached and forms a new independent individual.
(f) Vegetative propagation: When vegetative parts of a plant like stems, leaves and root etc., give rise to new ones, it is.called vegetative propagation.
Q.3. Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Ans.
Sexual reproduction means involvement of two parents in the process of reproduction. It is found mainly in higher plants where male gamete and female gamete fuse to form a zygote. These zygotes develop into individuals which are not identical. Offsprings inherit the characteristics of both the parents. In sexual reproduction both parents survive after the process of reproduction.
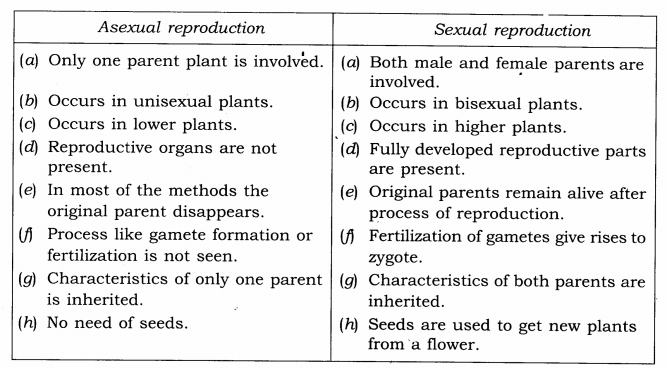
Q.4. State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Ans.
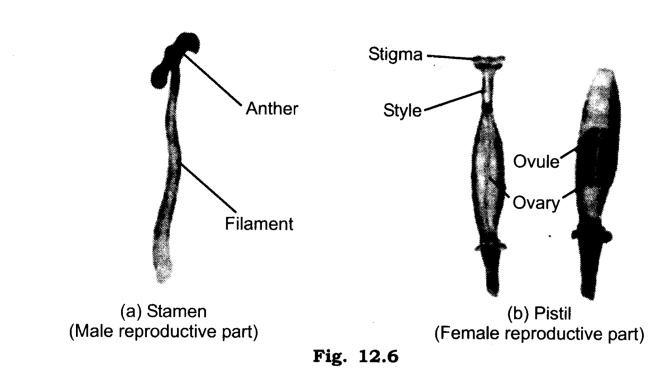
Q.5.Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Ans.
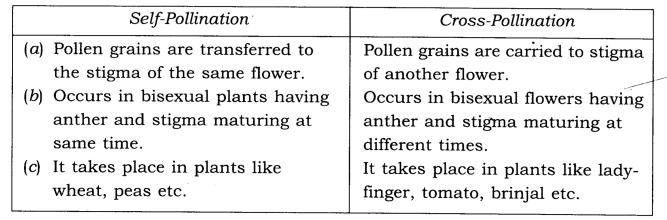
Q.6.Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination
Ans.
Q.7.How does the process of fertilization take place in flowers?
Ans.
When the pollen grain reaches the stigma of a same species flower, it starts
growing out into the pollen tube of the stigma. This tube continues to grow inside the style till it reaches the ovule. Male cells are released into the ovule for the fertilization with the female egg cell and thus the zygote is formed. After this process of fertilization, the ovary develops into fruit and ovule into seeds.
Q.8.Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Ans.
Following are the ways in which the seeds are dispersed:
(i) Some light seeds like that of madar, which are hairy, dry and small are carried away by the wind to different places.
(ii) Spiny seeds and fruits like that of xanthium and urena, stick to the clothes of passers by and animals. These seeds are carried away by these agents to different places.
(iii) In some plants having heavy seeds like that of coconut, water acts as the dispersing agents.
(iv) Some seeds are dispersed with the fruit burst like in case of balsam and castor.
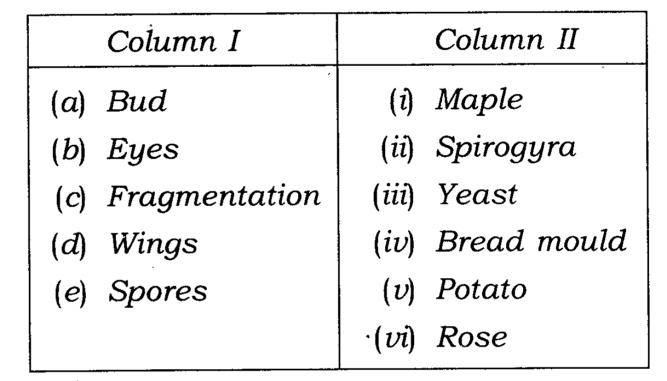
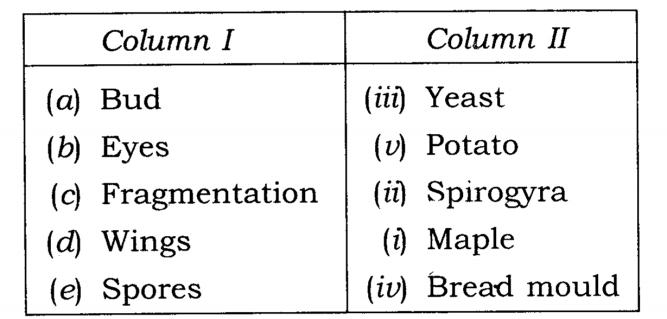
Q.9.Match items in Column I with those in Column II
Ans
Q.10. Tick (%/) the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf (ii) stem (iii) root (iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation (ii) pollination (iii) reproduction (iv) seed formation
c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed (ii) stamen (iii) pistil (iv) fruit
(d) A spore producing organism is
(i) rose (ii) bread mould (iii) potato (iv) ginger
(e) Bryophyllum can be reproduced by its
(i) stem (ii) leaves (iii) roots (iv) flower
Ans.
(a) (iv) flower (b) (i) fertilisation (c) (iv) fruit (d) (ii) bread mould (e) (ii) leaves

Leave a Reply