Solutions For All Chapters Science Class 7
Q.1. State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer.
Ans. Similarities:
(i) Both thermometers consist of long narrow uniform glass tubes.
(ii) Both have a bulb at one end.
(iii) Both contain mercury in bulb.
(iv) Both use Celsius scale on the glass tube.
Differences:
(i) A clinical thermometer reads temperature 35°C to 45°C while the range of laboratory thermometer is -10°C to 110°C.
(ii) Clinical thermometer has a kink near the bulb while there is no kink in the laboratory thermometer.
Due to kink mercury does not fall down on its own in clinical thermometer.
Q.2. Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
Ans. Conductors—aluminium, iron Insulators—plastic, wood.
Q.3.Fill in the blanks
(a) The hotness of an object is detetmined by its ____________ .
(b) Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a ____________ thermometer.
(c) Temperature is measured in degree ____________ .
(d) No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of ____________.
(e) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. It transfers heat to its other end by the process of ____________
(f) Clothes of ___________ colours absorb heat better than clothes of light colours.
Ans. (a) temperature (b) clinical (c) Celsius (d) radiation (e) conduction (f) dark
Q.5. Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing?
Ans. More layers of clothing keep us warm in winters as they have a lot of space between them. This space gets filled up with air. Air is a bad conductor, it does not allow the body heat to escape out.
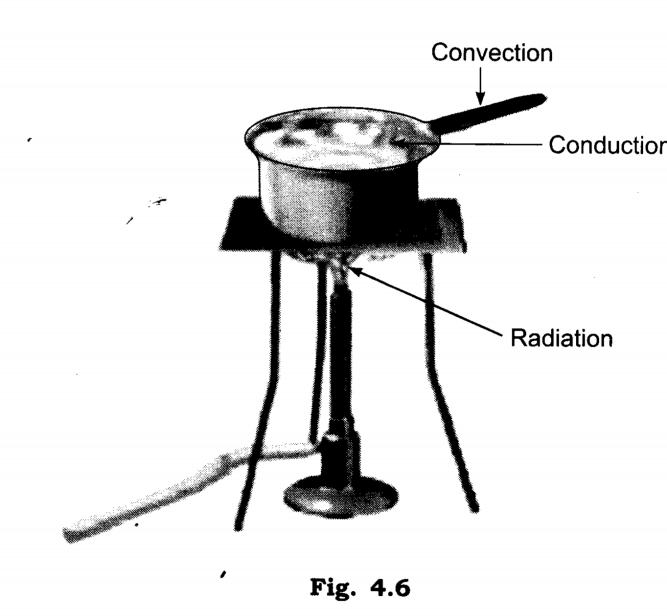
Q.6. Look at Fig. 3.13. Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation.
Ans.
Q.7. In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
Ans. In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer wall of houses be painted white because white colour reflects heat and the houses do not heat up too much.
Q.8. One litre of water at 30°C is mixed with one litre of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be:
(a) 80°C (b) More than 50°C but less than 80°C
(c) 20°C (d) Between 30°C and 50°C
Ans.(d) Between 30°C and 50°C.
Q.9. An iron ball at 40°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 40°C. The heat will:
(a) flow from iron ball to water.
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) flow from water to iron ball.
(d) increase the temperature of both.
Ans. (b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball
Q.10. A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice-cream. Its other end:
(a) becomes cold by the process of conduction
(b) becomes cold by the process of convection
(c) becomes cold by the process of radiation
(d) does not become cold
Ans. (d) does not become cold.
Q.11.Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that:
(a) copper bottom makes the pan more durable
(b) such pans appear colourful
(c) copper is a better conductor of heat than the stainless steel
(d) copper is easier to clean than the stainless steel
Ans.(c) copper is better conductor of heat than the stainless steel


Leave a Reply