Notes For All Chapters Science Class 7
Study Material and Notes of Ch 3 Fibre to Fabric Class 7th Science
Animal fibres
→ Wool and silk fibres are obtained from animals.
→ Wool is obtained from the fleece (hair) of fleece sheep or yak.
Silk fibres come from cocoons of the silk moth.
Wool
→ Wool comes from sheep, goat, yak and some other animals who are having hair on their body.
→ Wool is derived from these hairy fibres.
Animals that yield wool
→ Breeds of sheep are found in different parts of our country are the main source of obtaining wool.

• Yak wool: Obtained from Yaks which is common in Tibet and Ladakh.

• Angora wool: Obtained from Angora goats found in hilly regions such as Jammu and Kashmir.
• The under fur of Kashmiri goat is soft which is woven into fine shawls called Pashmina shawls.

• The fur (hair) on the body of camels.
• Llama and Alpaca, found in South America.

Rearing of Sheep and obtaining fibre
• Sheep are reared in hilly areas of Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim or the plains of Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
• Sheep are herbivores so mainly feed on grass and leaves. They are also provided pulses, corn, jowar, oil cakes and other materials.
• In winter, sheep are kept inside and fed leaves, grass and dry fodder.
• Sheep having thick coat of hair on their body yields good quality wool in large quantities.
• Hair of sheep is shaved off for getting wool, once the reared sheep have developed a thick growth of hair.
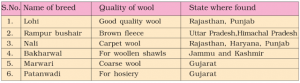
List of India breeds of sheep
Processing of Wool from Fibre
→ Obtaining wool is very long process which involves various steps.
Step 1(Shearing)

→ Fleece of the sheep along with a thin layer of skin is removed from its body which is called Shearing.
→ Shearing is done during hot weather so that sheep survive without protective hair.
→The hair or the fleece of the sheep are dead cells so it doesn’t hurt the sheep.
→ The instrument used to remove the fleece is similar to the shaving instrument.
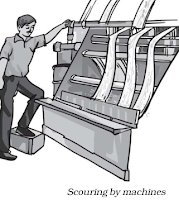
Step 2 (Scouring)

→ Washing of sheared skin with hair in tanks to remove grease, dust and dirt is called scouring. Nowadays scouring is done by machines.
Step 3 (Sorting)
→ The hairy skin is sent to a factory where hair of different textures are separated or sorted. This is called sorting.
Step 4
→ The small fluffy fibres, called burrs, are picked out from the hair. These are the same burrs which sometimes appear on your sweaters.
→The fibres are scoured again and dried. This is the wool ready to be drawn into fibres.
Step 5
→ The fibres can be dyed in various colours, as the natural fleece of sheep and goats is black, brown or white.
Step 6
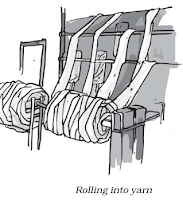
→ The fibres are straightened, combed and rolled into yarn.
→ The longer fibres are made into wool for sweaters and the shorter fibres are spun and woven into woollen cloth.
Silk
→ Silk fibres are also animal fibres. The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called sericulture.
Life history of silk moth
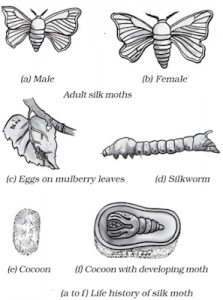
→ For obtaining silk, silkworms are reared on a large scale. A female silk moth gives hundreds of eggs on the mulberry leaf.
→ The eggs are then hatched by keeping them under the right temperature and humidity conditions.
→ Then, the silk caterpillars are fed on mulberry leaves. After 20-25 days, caterpillars stop eating and start spinning cocoons around them.
→ Further development of the moth continues inside the cocoon. The moth leaves the cocoon after its development is complete.
→ Once the moth has left the cocoon, it is collected to obtain silk.
→ The cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled or exposed to steam to separate the silk fibres. This process is known as reeling the silk.
→ Silk fibres obtained after reeling are spun into silk threads.
From cocoon to silk
→ For obtaining silk, moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk threads.
Rearing silkworms
→ A female silk moth lays hundreds of eggs at a time.
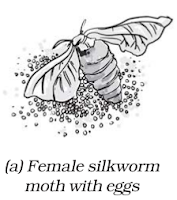
→ The eggs are stored carefully on strips of cloth or paper and sold to silkworm farmers.
→ The farmers keep eggs under hygienic conditions and under suitable conditions of temperature and humidity.
→ The eggs are warmed to a suitable temperature for the larvae to hatch from eggs.
→ This is done when mulberry trees bear a fresh crop of leaves.

→ The larvae, called caterpillars or silkworms, eat day and night and increase enormously in size.

→ The worms are kept in clean bamboo trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves.
→ After 25 to 30 days, the caterpillars stop eating and move to a tiny chamber of bamboo in the tray to spin cocoons.
→ Small racks or twigs may be provided in the trays to which cocoons get attached.
→ The caterpillar or silkworm spins the cocoon inside which develops the silk moth.
Processing silk
→ A pile of cocoons is used for obtaining silk fibres.
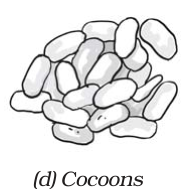
→ The cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled or exposed to steam.
→ The silk fibres separate out. The process of taking out threads from the cocoon for use as silk is called reeling the silk.
→ Reeling is done in special machines, which unwind the threads or fibres of silk from the cocoon.
→ Silk fibres are then spun into silk threads, which are woven into silk cloth by weavers.
NCERT Solutions of Fibre to Fabric Class 7

Leave a Reply