Solutions For All Chapters – Science Curiosity Class 7
The World of Metals and Non-metals
1. Which metal is commonly used to make food packaging materials as it is cheaper, and its thin sheets can be folded easily into any shape?
(i) Aluminium
(ii) Copper
(iii) Iron
(iv) Gold
Answer: (i) Aluminium
2. Which of the following metal catches fire when it comes in contact with water?
(i) Copper
(ii) Aluminium
(iii) Zinc
(iv) Sodium
Answer: (iv) Sodium
3. State with reason(s) whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F].
(i) Aluminium and copper are examples of non-metals used for making utensils and statues.
Answer: False
- Reason: Aluminium and copper are metals, not non-metals. They are lustrous, malleable, and good conductors, used for utensils and statues.
(ii) Metals form oxides when combined with oxygen, the solution of which turns blue litmus paper to red.
Answer: False
- Reason: Metal oxides are basic in nature and turn red litmus paper to blue, not blue litmus to red (which is a property of acidic substances).
(iii) Oxygen is a non-metal essential for respiration.
Answer: True
- Reason: Oxygen is a non-metal and is essential for respiration, as it is needed for living organisms to breathe and survive.
(iv) Copper vessels are used for boiling water because they are good conductors of electricity.
Answer: False
- Reason: Copper vessels are used for boiling water because copper is a good conductor of heat, not electricity, which helps in even heating.
4. Why are only a few metals suitable for making jewellery?
Answer: Only a few metals, like gold, silver, and platinum, are suitable for making jewellery because they are highly malleable and ductile, allowing them to be shaped into intricate designs. They are also lustrous, giving a shiny appearance, and resistant to corrosion, so they don’t tarnish easily.
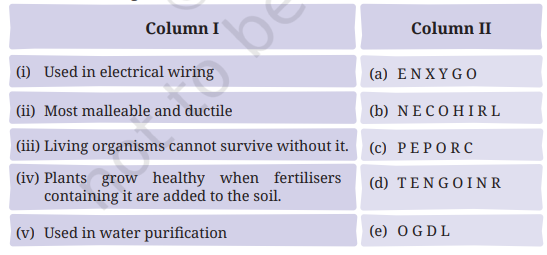
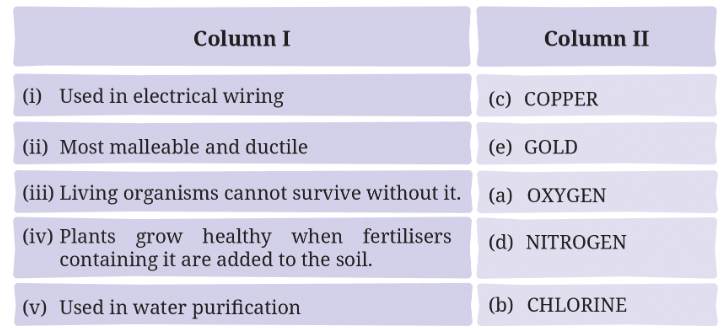
5. Match the uses of metals and non-metals given in Column I with the jumbled names of metals and non-metals given in Column II.
Answer:
6.What happens when oxygen reacts with magnesium and sulfur? What are the main differences in the nature of products formed?
Answer: When oxygen reacts with magnesium, it forms magnesium oxide, which is a basic oxide and turns red litmus paper to blue. However, when oxygen reacts with sulphur, it forms sulphur dioxide, which is an acidic oxide and turns blue litmus paper to red.
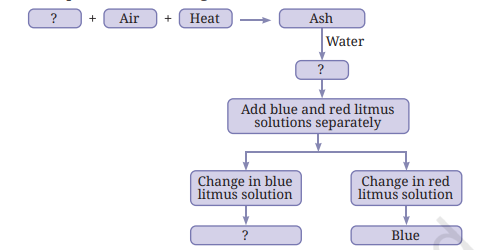
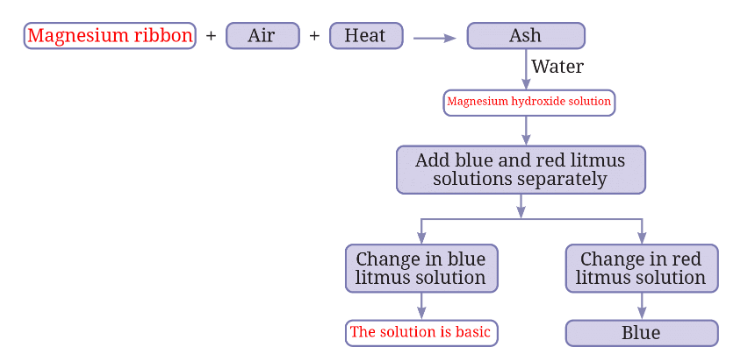
7. Complete the following flow chart:
Answer:
8. You are provided with the following materials. Discuss which material would be your choice to make a pan that is most suitable for boiling water and why?
Answer: I would choose copper to make a pan for boiling water. Copper is a metal and a good conductor of heat, ensuring even and quick heating. Unlike sulfur, coal, plastic, wood, or cardboard, copper is hard, durable, and can withstand high temperatures without melting or burning. Iron is also suitable but may rust, while copper resists corrosion better.
9. You are provided with three iron nails, each dipped in oil, water, and vinegar. Which iron nail will not rust, and why?
Answer: The iron nail dipped in oil will not rust. Rusting requires both water and air (oxygen) to occur. Oil forms a protective layer, preventing the nail from coming into contact with air and moisture, unlike water or vinegar, which allow rusting (vinegar may even speed it up due to its acidity).
10. How do the different properties of metals and non-metals determine their uses in everyday life?
Answer:
- Metals: Their properties like malleability (e.g., aluminium foil), ductility (e.g., copper wires), and good conductivity of heat (e.g., copper pans) and electricity (e.g., electrical wiring) make them ideal for utensils, wires, and tools. Their strength (e.g., iron in bridges) and sonority (e.g., bells) add to their uses.
- Non-metals: Non-metals like oxygen are essential for respiration, carbon is vital for life, nitrogen for fertilisers, and chlorine for water purification. Their poor conductivity (e.g., rubber in wire insulation) and acidic oxides (e.g., sulfur dioxide) suit specific applications.
11. One of the methods of protecting iron from getting rusted is to put a thin coating of zinc metal over it. Since sulfur does not react with water, can it be used for this purpose? Justify your answer.
Answer: Sulfur cannot be used to protect iron from rusting. Although sulfur does not react with water, it is a non-metal, brittle, and not suitable for coating as it cannot form a durable, protective layer like zinc (a metal). Zinc prevents rusting through galvanisation by acting as a sacrificial layer, while sulfur lacks the strength and adhesion needed for this purpose.
12.An ironsmith heats iron before making tools. Why is heating necessary in this process?
Answer: Heating iron is necessary because it makes the iron soft and malleable. When heated, iron becomes red-hot and easier to shape by hammering, allowing the ironsmith to would it into tools like axes or spades. This process uses iron’s malleability to create desired shapes.

Leave a Reply