Solutions For All Chapters – Science Curiosity Class 7
Changes Around Us: Physical and Chemical
1. Which of the following statements are the characteristics of a physical change?
(i) The state of the substance may or may not change.
(ii) A substance with different properties is formed.
(iii) No new substance is formed.
(iv) The substance undergoes a chemical reaction.
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii) (d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (c) (i) and (iii)
2. Predict which of the following changes can be reversed and which cannot be reversed. If you are not sure, you may write that down. Why are you not sure about these?
(i) Stitching cloth to a shirt
Answer: Stitching cloth to a shirt – Cannot be reversed: Once stitched, it is hard to undo without damage.
(ii) Twisting of straight string
Answer: Twisting of straight string – Can be reversed: The string can be untwisted.
(iii) Making idlis from a batter
Answer: Making idlis from a batter – Cannot be reversed: The batter cannot be returned to its original form after steaming.
(iv) Dissolving sugar in water
Answer: Dissolving sugar in water – Can be reversed: Sugar can be recovered by evaporating water.
(v) Drawing water from a well
Answer: Drawing water from a well – Can be reversed: Water can be returned to the well.
(vi) Ripening of fruits
Answer: Ripening of fruits – Cannot be reversed: Once ripe, fruits cannot go back to unripe.
(vii) Boiling water in an open pan
Answer: Boiling water in an open pan – Can be reversed: Evaporated water can be obtained back by condensation.
(viii) Rolling up a mat
Answer: Rolling up a mat – Can be reversed: The mat can be unrolled.
(ix) Grinding wheat grains to flour
Answer: Grinding wheat grains to flour – Cannot be reversed: Flour cannot be turned back into grains.
(x) Forming of soil from rocks
Answer: Forming of soil from rocks – Cannot be reversed: Soil formation is a slow process and cannot form rock back.
3. State whether the following statements are True or False. In case a statement is False, write the correct statement.
(i) Melting of wax is necessary for burning a candle. (True/False)
Answer: True
(ii) Collecting water vapour by condensing involves a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer: False
- Correct Statement: Collecting water vapour by condensing involves a physical change.
(iii) The process of converting leaves into compost is a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer: True
(iv) Mixing baking soda with lemon juice is a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer: True
4. Fill in the blanks in the following statements:
(i) Nalini observed that the handle of her cycle has got brown deposits. The brown deposits are due to rusting, and this is a chemical change.
(ii) Folding a handkerchief is a physical,change and can be reversed.
(iii) A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen with evolution of heat is called combustion, and this is a chemical change.
(iv) Magnesium, when burnt in air, produces a substance called magnesium oxide, The substance formed is basic, in nature. Burning of magnesium is a chemical change.
5. Are the changes of water to ice and water to steam, physical or chemical? Explain.
Answer: Physical
Explanation: Changing water to ice (freezing) or steam (evaporation/boiling) involves changes in state (solid to liquid or liquid to gas) without forming a new substance. No chemical reaction occurs, so these are physical changes.
6. Is curdling of milk a physical or chemical change? Justify your statement.
Answer: Chemical
Justification: Curdling of milk involves bacteria or acids reacting with milk to form curd, a new substance with different properties. This chemical reaction cannot be reversed, indicating a chemical change.
7. Natural factors, such as wind, rain, etc., help in the formation of soil from rocks. Is this change physical or chemical and why?
Answer: The formation of soil from rocks involves both physical and chemical changes. Natural factors like wind, rain and temperature break down rocks into smaller pieces (physical change), while chemical processes, like weathering, also change the minerals in the rocks (chemical change). Both types of changes work together to form soil.
8. Read the following story titled ‘Eco-friendly Prithvi’, and tick the most appropriate option(s) given in the brackets. Provide a suitable title of your choice for the story.
Prithvi is preparing a meal in the kitchen. He chops vegetables, peels potatoes, and cuts fruits (physical changes/chemical changes). He collects the seeds, fruits, and vegetable peels into a clay pot (physical change/chemical change). The fruits, vegetable peels, and other materials begin to decompose due to the action of bacteria and fungi, forming compost (physical change/chemical change). He decides to plant seeds in the compost and water them regularly. After a few days, he notices that the seeds begin to germinate and small
plants start to grow, eventually blooming into colourful flowers (physical change/chemical change). His eff orts are appreciated by all his family members.
Answer: Prithvi’s Green Kitchen
- Prithvi chops vegetables, peels potatoes, and cuts fruits – S physical changes
- He collects the seeds, fruits, and vegetable peels into a clay pot – V physical change
- He collects the seeds, fruits, and vegetable peels into a clay pot — V physical change
- The fruits, vegetable peels, and other materials decompose into compost — V chemical change
- Seeds germinate and grow into plants V chemical change
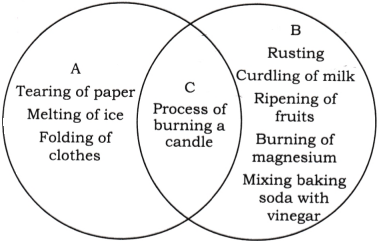
9. Some changes are given here. Write physical changes in the area marked ‘A’ and chemical changes in the area marked ‘B’. Enter the changes which are both physical and chemical in the area marked ‘C’. Process of burning a candle; Tearing of paper; Rusting; Curdling of milk; Ripening of fruits; Melting of ice; Folding of clothes; Burning of magnesium; Mixing baking soda with vinegar.
Answer:
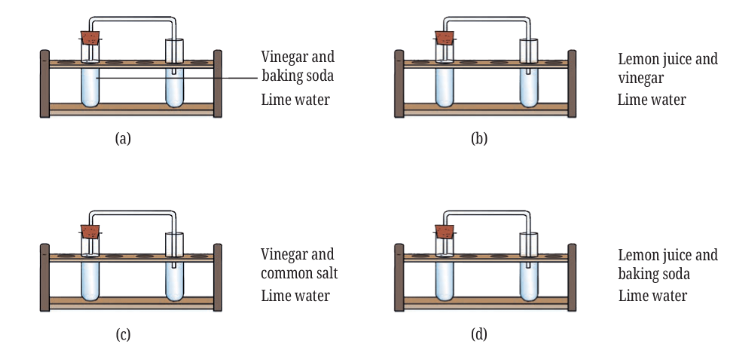
10. The experiments shown in Fig. 5.11a, b, c, and d were performed. Find out in which case(s) did lime water turn milky and why?
Answer: In Figure (a), when vinegar reacts with baking soda, carbon dioxide gas is released. This carbon dioxide gas travels through the straw into the test tube with lime water, where it reacts to form calcium carbonate, a white solid substance that makes the lime water appear milky.


That is very useful thank you. …………..,………………..,….,……..,……………