Solutions For All Chapters – Science Curiosity Class 7
Life Processes in Animals
1. Complete the journey of food through the alimentary canal by filling up the boxes with appropriate parts-
Food → Mouth → ______ → Stomach → ______ → ______ → Anus
Answer: Food → Mouth → Oesophagus → Stomach → Small Intestine → Large Intestine → Anus
2. Sahil placed some pieces of chapati in test tube A. Neha placed chewed chapati in test tube B, and Santushti took boiled and mashed potato in test tube C. All of them added a few drops of iodine solution to their test tubes-A, B, and C, respectively. What would be their observations? Give reasons.
Answer:
Observations and Reasons:
| Test Tube | Material Used | Expected Observation | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Chapati (unchewed) | Turns blue-black | Chapati contains starch, and iodine reacts with starch to give a blue-black color. |
| B | Chewed chapati | No color change or light blue-black | Saliva breaks down starch into sugar, so less or no starch remains to react with iodine. |
| C | Boiled & mashed potato | Turns blue-black | Potato also contains starch, which reacts with iodine to give a blue-black color. |
3. What is the role of the diaphragm in breathing?
(i) To filter the air
(ii) To produce sound
(iii) To help in inhalation and exhalation
(iv) To absorb oxygen
Answer: (iii) To help in inhalation and exhalation
4. Match the following.
| Name of the part | Functions |
|---|---|
| (i) Nostrils | (a) fresh air from outside enters |
| (ii) Nasal passages | (b) exchange of gases occurs |
| (iii) Windpipe | (c) protects lungs |
| (iv) Alveoli | (d) tiny hair and mucus help to trap dust and dirt from the air we breathe |
| (v) Ribcage | (e) air reaches our lungs through this part |
Answer:
| Name of the part | Functions |
| Nostrils | (a) fresh air from outside enters |
| Nasal passages | (d) tiny hair and mucus help to trap dust and dirt from the air we breathe |
| Windpipe | (e) air we breathe air reaches our lungs through this part |
| Alveoli | (b) exchange of gases occurs |
| Ribcage | (c) protects lungs |
5. Anil claims to his friend Sanvi that respiration and breathing are the same process. What question(s) can Sanvi ask him to make him understand that he is not correct?
Answer: Sanvi can ask the following questions to Anil to make him understand that breathing and respiration are not the same process:
- Do plants breathe? How do they get oxygen?
- Does the carbon dioxide we exhale come from respiration or breathing?
- Can we perform respiration without breathing for a short time?
- Can you give an example of a process that involves breathing but not respiration?
6. Which of the following statements is correct and why?
Anu: We inhale air.
Shanu: We inhale oxygen.
Tanu: We inhale air rich in oxygen.
Answer: Tanu’s statement is correct: We inhale air rich in oxygen. When we inhale, we take in air that contains about 21% oxygen and exhale air having more carbon dioxide than inhaled air.
7. We often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air. What can be possible explanations for this?
Answer: When we inhale a lot of dust-laden air, the dust particles get trapped in the hair of our nasal cavity. These particles irritate the lining of the cavity. As a result, we sneeze to expel these dust particles. Sneezing expels these foreign particles from the inhaled air, and dust-free, clean air enters our bodies.
8. Paridhi and Anusha of Grade 7 started running for their morning workout. After they completed their running, they counted their breaths per minute. Anusha was breathing faster than Paridhi. Provide at least two possible explanations for why Anusha was breathing faster than Paridhi.
Answer:
- Anusha may have run faster or covered a longer distance than Paridhi, causing her body to require more oxygen, which leads to faster breathing.
- Anusha might have lower stamina or be less physically fit than Paridhi, making her body work harder during the run, resulting in faster breathing to meet the oxygen demand.
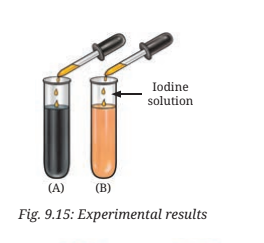
9. Yadu conducted an experiment to test his idea. He took two test tubes, A and B, and added a pinch of rice flour to the test tubes, half filled with water and stirred them properly. To test tube B, he added a few drops of saliva. He left the two test tubes for 35-45 min. After that, he added iodine solution into both the test tubes. Experimental results are as shown in Fig. 9.15. What do you think he wants to test?
Answer : Yadu wanted to test whether saliva breaks down starch into sugar.
Explanation:
- Test Tube A turned blue-black after adding iodine, indicating the presence of starch.
- Test Tube B showed no color change or a lighter color, meaning the starch was broken down by the saliva.
This proves that saliva contains enzymes (like salivary amylase) that help digest starch into sugar.
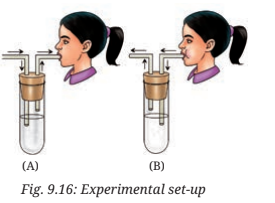
10. Rakshita designed an experiment taking two clean test tubes, A and B and filled them with lime water as shown in the figure. In test tube A, the surrounding air that we inhale was passed on by sucking air from the pipe, and in test tube B, the exhaled air was blown through the pipe (Fig. 9.16). What do you think she is trying to investigate? How can she confirm her findings?
Answer: Rakshita is trying to investigate the gas we inhale and exhale while breathing. The lime water in test tube B turned milky (or cloudy), but the lime water in test tube A did not. Lime water turns milky when it reacts with carbon dioxide. Therefore, this indicates that the exhaled air contains more carbon dioxide than the air we inhaled.

The answers are great for exams, but how can I remember them?
The answer is too lengthy
The answer is too lengthy