Notes For All Chapters – Social Science Class 6
Grassroots Democracy – Part 1: Governance
- Protection of Dharma:
- “The ruler protects dharma, and dharma protects those who protect it” (Mahābhārata).
- This highlights the mutual responsibility between rulers and justice.
Introduction
- Justice and Equality:
- “No peace without justice; no justice without equality” (Rigoberta Menchú Tum).
- Equality, justice, and development are interlinked for societal harmony.
- Need for Rules:
- In any community or group, rules are necessary to maintain order and harmony.
- Examples of rules exist at home, schools, workplaces, and public spaces (e.g., traffic rules).
- Function of Rules:
- Without rules, society would descend into chaos, making orderly functioning impossible.
- Governance and Government:
- Governance: The process of creating and implementing rules for societal organization.
- Government: The system or group that creates and enforces these rules. Important rules are referred to as laws.
- Adaptability of Rules:
- Rules and laws are not fixed; citizens can influence changes, much like how discussions occur within families or schools to adjust rules.
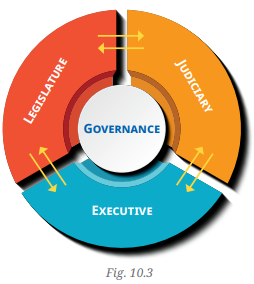
Three Organs of Government
Impact of Digital Technologies:
- Digital transformation has reshaped how societies function globally, including in India.
- About 30 years ago, people used methods like money orders and demand drafts for financial transactions, which were time-consuming.
- Today, digital means allow instant money transfers, eliminating the need for such outdated practices.
- Emergence of Cybercrime:
- The rise of digital technology has led to new types of crimes, known as cybercrime.
- Criminals use digital methods to steal money without physically committing theft.
- Governments have responded by passing new laws to combat these criminal activities.
- Role of Law Enforcement:
- Cybercriminals who steal money using digital means are tracked, arrested, and convicted.
- They face penalties such as fines and jail time for their illegal activities.
- Three Organs of Government:
- Legislature:
- Responsible for making and updating laws.
- This body consists of representatives of the people who gather to legislate.
- In response to new challenges like cybercrime, the legislature creates new laws or modifies existing ones.
- Executive:
- Responsible for implementing and enforcing laws.
- Includes the head of state (President, Prime Minister, or Chief Minister), ministers, and law enforcement agencies (like cyber police in this case).
- The executive ensures that laws are applied effectively, maintaining law and order.
- Judiciary:
- The system of courts that interprets the laws and determines if someone has violated them.
- Courts decide appropriate punishments for lawbreakers and can review executive actions and legislative laws to ensure fairness.
- The judiciary also checks the legality and fairness of decisions made by the executive and legislature.
- Legislature:
- Separation of Powers:
- The separation of powers ensures that the three organs of government (legislature, executive, and judiciary) remain distinct.
- Although they interact and work together, each organ has a specific role, preventing any one branch from overreaching.
- This system provides checks and balances, meaning that each organ monitors the others to maintain a balanced governance system and prevent misuse of power.
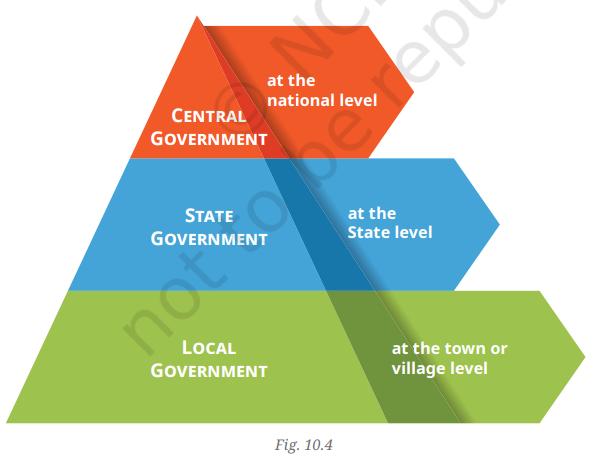
Three Levels of Government
- Levels of Government:
- Governments function at multiple levels: local, state, and national.
- Each level is responsible for specific issues, similar to how problems are addressed at home, with an electrician, or by the Electricity Board.
- In India, the three levels are:
- Local Government: Manages local issues.
- State Government: Handles state-level concerns.
- Central or Union Government: Manages national-level issues.
- Example of Flood Management:
- Local authorities manage minor floods in limited areas.
- State government steps in when floods affect multiple towns and villages.
- The Central government provides support (e.g., relief supplies, army assistance) during large-scale floods.
- Mottos Inspired by Ancient Wisdom:
- Government of India’s Motto: Satyameva Jayate – “Truth alone triumphs.”
- Supreme Court’s Motto: Yato Dharmastato Jayah – “Where there is dharma, there is victory.”
- Functions and Responsibilities of the Government at Various Levels:
- Judiciary:
- National: Supreme Court of India.
- State: High Court.
- Legislature:
- National: Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha (two houses) formulate national laws.
- State: Vidhan Sabha (State Assembly) formulates state laws.
- Executive:
- National:
- Led by the President (nominal head and Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces).
- Prime Minister is the executive head.
- State:
- Led by the Governor (nominal head).
- Chief Minister is the executive head.
- National:
- Judiciary:
- Key Functions and Responsibilities of the Executive:
- Central Government: Handles defence, foreign affairs, atomic energy, communications, currency, interstate commerce, national policy formulation.
- State Government: Manages police and law and order, education, agriculture, irrigation, public health, and adaptation/implementation of central laws at the state level.
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam – A National Inspiration:
- Background: Born in 1931 in Rameswaram, Tamil Nadu; a renowned scientist known as the ‘Missile Man of India.’
- Career: Contributed to India’s space and missile programs and served as the 11th President of India (2002-2007).
- Impact: Deeply connected to the people, especially the youth, advocating for education, innovation, and dreaming big.
- Inspiring Thoughts:
- “Dreams are those that don’t let you sleep.”
- “Failure is the ‘First Attempt In Learning’ (F.A.I.L.).”
- “To succeed, one must have single-minded devotion.”
- “If you get a ‘No’, it means ‘Next Opportunity’ (N.O.).”
- Dr. Kalam’s Lessons for Success:
- Aim high.
- Acquire knowledge.
- Work hard.
- Persevere to achieve anything.
Democracy
- Definition of Democracy:
- Democracy derives from two Greek words: dēmos (people) and kratos (rule or power), meaning “rule of the people.”
- It is the system of governance where citizens have the power to elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf.
- Representation in Democracy:
- All citizens cannot rule directly; hence, they elect representatives to govern.
- Example: In a school, a class elects a monitor or representative to communicate with the principal.
- At the state level, representatives are called Members of Legislative Assembly (MLAs).
- At the national level, representatives are known as Members of Parliament (MPs).
- Decision-Making Process:
- Representatives in assemblies discuss laws, problems, and solutions through dialogue and debate.
- They aim to convince each other when differing opinions arise, forming the foundation of democratic governance.
- India as a Representative Democracy:
- India is the world’s largest democracy, with approximately 970 million voters in 2024.
- All Indian citizens above 18 years of age have the right to vote in elections, participating in the democratic process.
- Direct Democracy Example:
- In a class setting, if students vote on a location for a picnic, the decision is made by counting the raised hands for two options (A or B). This is a form of direct democracy.
- Every student’s opinion is taken into account, illustrating participation in decision-making.
- Grassroots Democracy:
- Grassroots democracy refers to systems that encourage the participation of ordinary citizens at the local level.
- Citizens, especially at the base of society, are empowered to have a say in decisions affecting their lives.
- Key Features of Governance in Democracy:
- No country can function without governance and government.
- A modern government has three key organs:
- Legislative: Makes laws.
- Executive: Implements laws.
- Judiciary: Interprets and enforces laws.
- Three Levels of Government:
- The Indian government operates at three levels:
- Centre/National level.
- State level.
- Local level.
- The Indian government operates at three levels:
- Overall Framework:
- Democracy is the overarching framework within which governance operates in India, functioning through elected representatives at both state and national levels.



too lenghty but have great information
please make them bit shorter