Notes For All Chapters – Social Science Class 6
Grassroots Democracy — Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas
Introduction
Local Governance Desire:
- Rustom K. Sidhwa, during the Constituent Assembly debates (October 13, 1949), expressed the desire for immediate formation of full-fledged local bodies. He emphasized the importance of local administration, understanding franchise, powers, rights, and privileges in villages and towns.
Democratic Governance:
- Democracy aims to empower citizens by encouraging active participation in governance across various levels, from rural to national. This is known as participatory democracy.
Rural and Urban Governance:
- While rural governance was previously discussed, urban governance is more complex and diverse. Therefore, urban governance systems need to be more intricate to address the challenges of urban areas.
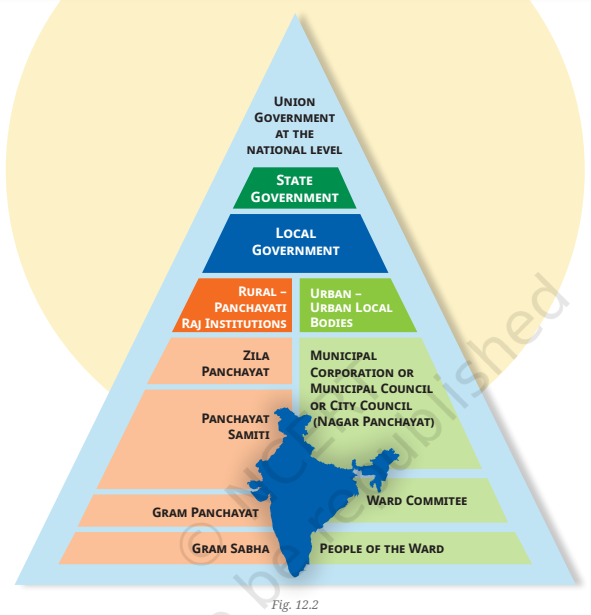
Pyramid Structure of Governance:
- Governance in India can be visualized as a pyramid, with the local level at the base (closer to the people) and the national level at the top. The governance system moves from rural to urban and national, each requiring different levels of complexity in administration.
Urban Local Bodies
- Definition of Urban Local Bodies (ULBs):
- ULBs are decentralized governance structures in urban areas, meaning local communities have direct input on how their areas are managed.
- They enable citizens to come together and make decisions for their local area, empowering local participation.
- Wards and Committees:
- Urban areas are divided into smaller units called wards.
- Ward committees are responsible for local activities like organizing health camps, anti-plastic campaigns, and addressing infrastructural issues (e.g., water leaks, blocked drains).
- The precise functions of wards vary by state due to differing rules.
- Functions of Urban Local Bodies:
- ULBs handle a range of responsibilities, including:
- Infrastructure maintenance (roads, drains, etc.).
- Garbage collection and disposal.
- Managing burial grounds.
- Monitoring the implementation of government schemes.
- Collecting local taxes and fines.
- They also contribute to the economic and social development of their areas.
- ULBs handle a range of responsibilities, including:
- Citizens’ Duties in a Participatory Democracy:
- Citizens must actively perform their duties to ensure the efficiency of ULBs. This includes:
- Segregating waste to simplify garbage collection.
- Reporting issues like water leakages promptly to prevent wastage.
- Citizens must actively perform their duties to ensure the efficiency of ULBs. This includes:
- History of Municipal Corporations:
- The Madras Corporation (now Greater Chennai Corporation) is the oldest municipal institution in India, established on 29 September 1688.
- A Parliamentary Act in 1792 empowered the Madras Corporation to levy municipal taxes, marking the beginning of municipal administration.
- Types of Urban Local Bodies:
- Cities with populations above 10 lakhs have a Municipal Corporation (Mahanagar Nigam).
- Cities with populations between 1 and 10 lakhs have a Municipal Council (Nagar Palika).
- Smaller towns and cities have a Nagar Panchayat.
- Urban and Rural Governance Comparison:
- Urban local governance is more complex due to the size and diversity of urban areas.
- Both urban and rural areas have elected representatives who work to address local concerns.
- Participatory Democracy in Action:
- Citizens’ voices are important in urban and rural governance.
- Example dialogue shows how both urban and rural areas engage in local governance, from reporting infrastructure issues in a village to collective action during emergencies in cities.
- Key Takeaways:
- Urban local bodies play a vital role in decentralized governance, impacting many aspects of city life.
- Like rural areas, urban areas have elected representatives, and citizen participation is essential for efficient governance.
- Citizens’ engagement, like waste segregation and reporting issues, helps local bodies perform their duties effectively.


Very good notes
Nice
Wonderful