Notes For All Chapters – Social Science Class 6
Oceans and Continents
The Blue Planet: Earth
Earth’s Predominant Color:
- When viewing the Earth from space, the most noticeable color is blue.
- The blue color represents water, which covers nearly three-fourths of Earth’s surface.
- This abundance of water gives Earth its characteristic appearance as a “blue planet.”
- Early astronauts affectionately named Earth the “blue planet” due to its appearance from space.
Oceans and Landmasses
Oceans:
- The largest bodies of water visible on Earth are called oceans.
- Oceans are the most significant water bodies, covering the majority of the Earth’s surface.
- Oceans play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate and supporting life.
Land:
- The brown color visible on the globe represents land, which covers just over one-fourth of Earth’s surface.
- A large body of land is referred to as a “landmass.”
- A continuous expanse of land is termed a “continent.”
- Both landmasses and oceans significantly influence the Earth’s climate, affecting all living organisms, including humans.
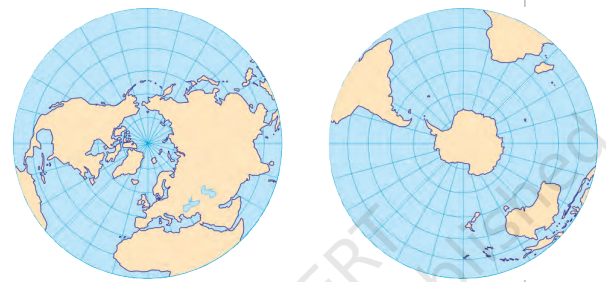
Distribution of Water and Land
Unequal Distribution:
- Water and land are not evenly distributed between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
- The maps indicate that the blue areas consist of oceans and their smaller extensions like seas, bays, and gulfs.
Water Resources:
- Oceans hold the majority of Earth’s water, but this seawater is salty and unsuitable for most land animals, including humans.
- Freshwater, essential for human consumption, is limited and found in glaciers, rivers, lakes, the atmosphere, and underground as groundwater.
Importance of Oceans and Continents
Impact on Climate and Life:
- Oceans and continents have a vital role in shaping Earth’s climate.
- They influence all aspects of life, from plants and animals to human societies.
- Their effects are evident in human history, culture, and daily life.
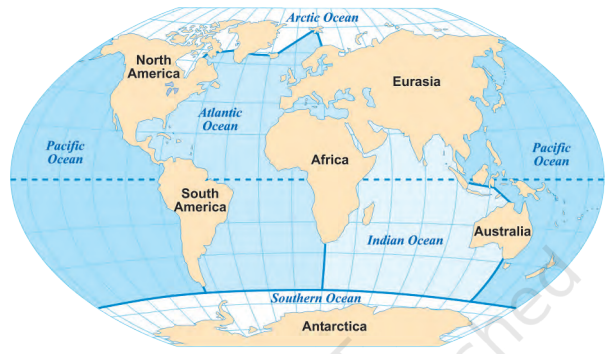
Oceans of the World
Five Major Oceans:
- The world map displays five oceans:
- Pacific Ocean
- Atlantic Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- Arctic Ocean
- Southern (Antarctic) Ocean
- These oceans are not truly separate; the divisions on the map are man-made conventions.
- Seawater flows continuously across these oceans, supporting a rich diversity of marine life.
Marine Biodiversity:
- Marine Flora: Includes tiny plants like algae and various types of seaweeds.
- Marine Fauna: Consists of thousands of species of fish, dolphins, whales, and mysterious deep-sea creatures.
- Each layer of the ocean, from the sunlit surface to the dark depths, hosts unique and diverse life forms.
Oceans and Natural Disasters
Cloud Formation and Rainfall:
- Oceans play a crucial role in cloud formation, which is visible as white shapes across the globe.
- These clouds are responsible for bringing rain to continents, essential for agriculture and sustaining life.
- For example, the monsoon rains in India originate from the ocean, vital for the country’s agriculture.
Ocean-Related Disasters:
Cyclones:
- Oceans can give rise to violent storms with extreme rainfall or strong winds, known as cyclones.
- Cyclones can cause significant damage, especially to coastal regions around the world.
Tsunamis:
- Tsunamis are powerful, large waves usually triggered by strong earthquakes or volcanic eruptions at the ocean’s bottom.
- Tsunamis can travel thousands of kilometers, submerging coastal areas and causing widespread devastation.
Continents of the World
Visibility on Maps:
- Continents are clearly visible on the world map alongside the oceans.
- The number of continents can be counted in various ways, leading to different totals ranging from four to seven.
Different Ways to Count Continents:
Four Continents:
- Africa-Eurasia, America, Antarctica, Australia.
- Africa-Eurasia is a combined landmass of Africa, Europe, and Asia.
- America combines North and South America as a single continent.
Five Continents:
Africa, America, Antarctica, Australia, Eurasia.
Eurasia is a combination of Europe and Asia.
America is counted as a single continent.
Continents of the World
Visibility on Maps:
- Continents are clearly visible on the world map alongside the oceans.
- The number of continents can be counted in various ways, leading to different totals ranging from four to seven.
Different Ways to Count Continents:
Four Continents:
- Africa-Eurasia, America, Antarctica, Australia.
- Africa-Eurasia is a combined landmass of Africa, Europe, and Asia.
- America combines North and South America as a single continent.
Five Continents:
- Africa, America, Antarctica, Australia, Eurasia.
- Eurasia is a combination of Europe and Asia.
- America is counted as a single continent.
Six Continents:
- Africa, Antarctica, Australia, Eurasia, North America, South America.
- North America and South America are counted as separate continents.
Seven Continents (Most Widely Accepted):
- Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, South America.
- Europe and Asia are treated as distinct continents despite forming a single landmass.
Continental Divisions and Reasons:
North America and South America:
Generally considered two continents but can be seen as one when viewed as a single landmass.
Europe and Asia:
Typically counted as two continents due to different historical and cultural developments, but geologists often combine them into one continent called Eurasia.
Africa and Eurasia:
Typically regarded as two separate continents, but they can sometimes be seen as a single landmass.
Olympic Rings and Continents:
The five Olympic rings symbolize the coming together of athletes from five inhabited continents: Africa, America, Asia, Australia, and Europe.
Representation in Diagrams:
The diagram on page 36 (not shown here) is based on the list of seven continents and depicts their relative sizes rather than their actual shapes.
Islands
Definition:
- Islands are smaller landmasses surrounded by water on all sides, distinct from continents due to their smaller size.
- Unlike continents, islands are not large enough to be considered part of a continent.
Distribution:
- There are hundreds of thousands (lakhs) of islands on Earth, varying greatly in size.
Oceans and Life
Role in the Environment:
- Water Cycle:
- Oceans are integral to the Earth’s water cycle, contributing to rainfall on continents.
- Without oceans, there would be no rainfall, turning Earth into a desert.
- Oxygen Production:
- Oceans produce more than half of the world’s oxygen through their flora, earning the title “the planet’s lungs.”
- This oxygen production is essential for life on Earth.
Climate Regulation:
- Oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate by distributing heat and moisture globally.
- The presence of oceans is vital for maintaining the balance needed to sustain life.
Human Interaction with Oceans:
Historical Impact:
- Throughout history, oceans have been used for migration, trade, military campaigns, and as a food source through fishing.
- Oceans have deeply influenced the cultures of coastal communities worldwide.
Cultural Significance:
- Many coastal cultures have myths, legends, and folklore related to the sea, including tales of sea gods, goddesses, monsters, and treasures.
- These stories reflect both the dangers and the blessings that oceans have brought to humanity.
Key Takeaways
Surface Composition:
- The Earth’s surface consists of vast water bodies called oceans and large landmasses called continents.
- Oceans are interconnected, and continents can be counted in various ways, with seven being the most common count.
Geographical Distribution:
- The Northern Hemisphere contains more land than the Southern Hemisphere.
Environmental Importance:
- Oceans are vital for supporting marine life and play a critical role in regulating the world’s climate.
- They are currently under threat from human activities and require collective efforts for protection.

Leave a Reply