Notes For All Chapters – Social Science Class 6
Family and Community
- Love and Dharma: Fundamental aspects of family life (as per Tiruvalluvar).
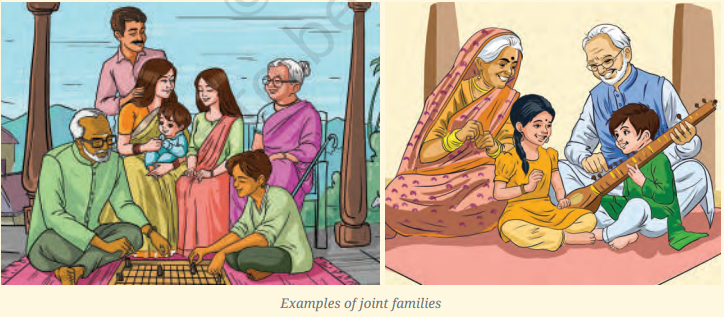
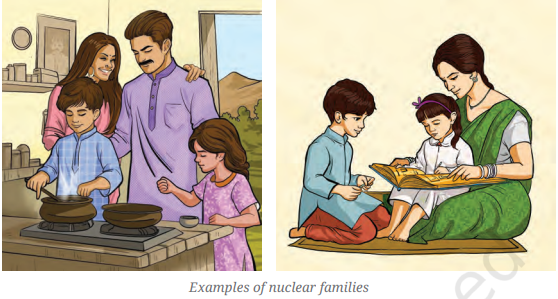
- Family: The basic and oldest social unit; different types exist in Indian society.
- Joint Family: Includes multiple generations living together (grandparents, parents, uncles, aunts, siblings, cousins).
- Nuclear Family: Limited to a couple and their children, sometimes only one parent with children.
Family
- English has limited terms for family relations.
- Indian languages have specific terms like bua, tau, chacha, mausi in Hindi.
- Tamil distinguishes elder and younger siblings with different terms.
- No specific word for ‘cousin’ in most Indian languages as cousins are considered brothers and sisters, showing stronger family bonds.




Leave a Reply