Solutions For All Chapters – Social Science Class 6
Locating Places on the Earth
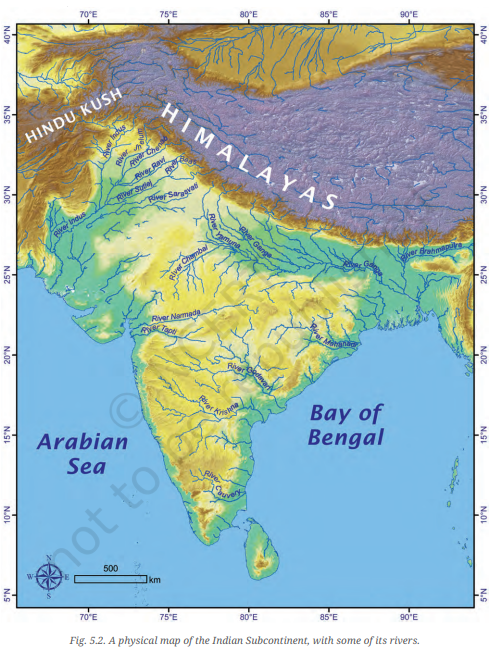
Question 1. Returning to page 10 and to Fig. 5.2 in Chapter 5 of this textbook, taking the scale to be 2.5 cm = 500 km, calculate the real distance from the estuary of the Narmada River to the estuary of the Ganga river. (Hint: round off your measurement on the map to an easy number.)
Answer:
- Reference: You are asked to refer to a map on page 10, Fig. 5.2, where the scale is 2.5 cm = 500 km.
- Step-by-Step Solution:
- First, measure the distance between the estuaries of the Narmada River and the Ganga River on the map in centimeters.
- Suppose the distance on the map is 4 cm.
- Using the scale provided (2.5 cm = 500 km), calculate the real distance:
Real Distance = ( \( \frac{Measured Distance (cm)}{2.5} \)) x 500 km
Real Distance = ( \( \frac{4 cm}{2.5} \)) x 500 km = 2 x 500 km = 1000 km
Therefore, the real distance between the estuaries of the Narmada River and the Ganga River is approximately 1000 km.
Question 2. Why is it 5:30 pm in India when it is 12 pm or noon in London?
Answer:
- India is located at a longitude of about 82.5°E, and London (Greenwich) is at 0° longitude.
- The Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, which means it rotates 15° in 1 hour.
- Since India is east of Greenwich, time is ahead in India. To calculate the time difference:
Time Difference = ( \( \frac{82.5 °E – 0°}{15°/hour} \)) = 5.5 hours
- Therefore, when it is 12 pm (noon) in London, it is 5:30 pm in India, which is 5.5 hours ahead due to the longitude difference.
Question 3. Why Do We Need Symbols and Colours in the Map?
Answer: Symbols and colours on maps serve to represent various physical and human-made features in a simplified and standardized way.
- Symbols: They represent objects like roads, rivers, schools, and hospitals, making it easy to understand and interpret the map. Without symbols, maps would be cluttered and confusing.
- Colours: Different colours represent various natural features like mountains, forests, and water bodies. Colours make the map visually easier to read and help in quickly identifying different types of areas.
Overall, symbols and colours are essential for clarity and ease of understanding.
Question 4. Find Out What You Have in the Eight Directions from Your Home or School.
Answer: To find out what lies in the eight directions (North, South, East, West, Northeast, Southeast, Southwest, Northwest) from your home or school:
- Use a compass to determine the exact directions.
- Identify key landmarks or features in each of the eight directions.
- For example:
- North: Park
- Northeast: Shopping mall
- East: Railway station
- Southeast: School
- South: River
- Southwest: Market
- West: Residential area
- Northwest: Hospital
Discuss these findings in class to see how different environments affect what is located in each direction.
Question 5. What is the Difference Between Local Time and Standard Time? Discuss it in groups, with each group writing an answer in 100 to 150 words. Compare the answers.
Answer:
- Local Time: This is the time based on the position of the sun in the sky relative to a specific location. It varies from place to place based on the longitude.
- Standard Time: This is the uniform time set for a specific region or country. It is based on a standard meridian and is used across various time zones within the country.
- Difference: Local time can differ for different places within the same time zone, while standard time is consistent across the entire time zone. In India, for example, Indian Standard Time (IST) is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT and is applied uniformly across the country, despite the longitudinal differences from Gujarat to Assam.
Summary: Local time varies by longitude, while standard time is a consistent, agreed-upon time for an entire region or country.
Question 6. Delhi’s and Bengaluru’s latitudes are 29°N and 13°N; their longitudes are almost the same, 77°E. How much will be the difference in local time between the two cities?
Answer:
- Delhi’s Latitude: 29°N
- Bengaluru’s Latitude: 13°N
- Longitude of Both Cities: Approximately 77°E
Understanding Time Difference:
- Longitude is the key factor in determining time differences because the Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, which means 15° of longitude corresponds to a 1-hour time difference.
- Since Delhi and Bengaluru are located at nearly the same longitude (77°E), the time difference between them based on longitude is negligible.
Latitude and Time:
- Latitude affects the climate and the length of daylight but does not directly affect the local time. Therefore, the difference in latitude between Delhi and Bengaluru (29°N vs. 13°N) does not result in a time difference.
Conclusion:
- Difference in Local Time: There is no difference in local time between Delhi and Bengaluru because they share nearly the same longitude. The latitude difference does not influence local time. Both cities follow the same local time.
Question 7. Mark the following statements as true or false; explain your answers with a sentence or two.
(a) All parallels of latitude have the same length.
Answer: False: Parallels of latitude are circles that run east-west around the Earth. The length of these circles decreases as you move from the Equator toward the poles. The Equator is the longest parallel of latitude, while the poles (90°N and 90°S) are points rather than circles, so they have no length.
(b) The length of a meridian of longitude is half of that of the Equator.
Answer: True: A meridian of longitude runs from the North Pole to the South Pole, making it half the length of the Equator, which is a full circle around the Earth.
(c) The South Pole has a latitude of 90°S.
Answer: True: The South Pole is located at the southernmost point of the Earth, which corresponds to a latitude of 90°S.
(d) In Assam, the local time and the IST are identical.
Answer: False: Assam is located in the eastern part of India, where the local time would naturally be ahead of IST due to its position relative to the Prime Meridian. However, India follows a single time zone, IST (Indian Standard Time), which is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of GMT. Therefore, Assam’s local time is not the same as IST, but the entire state follows IST for uniformity.
(e) Lines separating the time zones are identical with meridians of longitude.
Answer: True: Time zones are spaces of 15° of longitude that change by one hour with regard to the local time. As the circle has 360°, there are 24 time zones pertaining to 24 hours that are in a day. Thus time zones are identical with meridian of longitude – 0°, 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75°, till 180° Eastwards and Westwards.
(f) The Equator is also a parallel of latitude.
Answer: True: The Equator is the most significant parallel of latitude, located at 0° latitude. It is the longest parallel and divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
(g) Solve the crossword below.
Across
1. Lets you squeeze a huge area into your map
4. A convenient sphere
5. The longest parallel of latitude
6. The place the Prime Meridian is attached to
8. So convenient to find your way
10. A measure of the distance from the Equator
Down
2. A measure of the distance from the Prime Meridian
3. These two together allow us to locate a place
6. What latitudes and longitudes together create
7. The time we all follow in India
9. These two are poles apart
11. An abbreviation for a line across which the day and date change
Answer:
The Big Questions (Page 7)
Question 1. What is a map and how do we use it? What are its main components?
Answer: A map is a visual representation of an area, showing the relationships between different elements like roads, landmarks, and geographical features. We use maps to navigate, locate places, and understand spatial relationships. The main components of a map are distance (scale), direction, and symbols.
Question 2. What are coordinates? How can latitude and longitude be used to mark any location on the Earth?
Answer: Coordinates are a system of numbers used to specify the position of a point on the Earth’s surface. Latitude and longitude are two types of coordinates: latitude measures how far north or south a point is from the Equator, and longitude measures how far east or west a point is from the Prime Meridian. Together, they can precisely identify any location on Earth.
Question 3. How are local time and standard time related to longitude?
Answer: Local time is determined by the position of the Sun in the sky at a specific longitude. As the Earth rotates, different longitudes experience different times of day. Standard time is a uniform time adopted across a region or country, typically based on the time at a specific central longitude. This helps maintain consistency across time zones within a country or region.

Very good for study
Best
Excellent