Solutions For All Chapters – Social Science Class 6
Timeline and Sources of History
Question 1. As a project, write the history of your family (or village if you live in one), using sources of history at your disposal. Ask your teacher to guide you.
Answer: We live in a small village called Roshanpur in U.P. Through the Gram Panchayat we came to know various historical facts about the village. The village ancestors first moved in around 1500 years back, i.e., around 500 A.D.
Question 2. Can we compare historians to detectives? Give reasons for your answers.
Answer: Yes, historians can be compared to detectives for several reasons including their Investigative approach, their way of analysing evidence, the way they construct narratives, the manner they give attention to detail and also for their problem-solving skills. We can further detail this as
| Aspect | Historians | Detectives |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Study and interpret past events and societies. | Solve crimes and uncover facts related to specific cases. |
| Sources of Information | Historical documents, artifacts, oral histories, and other sources from the past. | Physical evidence, witness statements, forensic data, and other crime-related materials. |
| Objective | To understand and explain how and why events happened in the past. | To find the perpetrator of a crime and establish what happened. |
| Methodology | Research, analysis of multiple sources, and interpretation based on context. | Investigation, gathering evidence, questioning witnesses, and logical deduction. |
| Outcome | A historical narrative or interpretation that helps explain the past. | A conclusion that leads to the resolution of a case, such as identifying the guilty party. |
Question 3. A few exercises with dates:
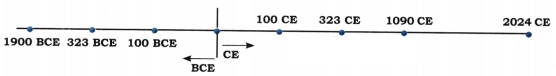
(a) Place these dates chronologically on the timeline: 323 CE, 323 BCE, 100 CE, 100 BCE, 1900 BCE, 1090 CE, 2024 CE.
Answer:
(b) If King Chandragupta was born in 320 CE, which century did he belong to? And how many years was that after the Buddha’s birth?
Answer:
- Century: King Chandragupta was born in the 4th century CE.
- Years after Buddha’s birth: Buddha was born around 560 BCE. To calculate the number of years after Buddha’s birth:
320 CE + 560 BCE − 1 = 879 years after Buddha’s birth
(c) Rani of Jhansi was born in 1828. Which century did she belong to? How many years was that before India’s Independence?
Answer:
- Century: Rani of Jhansi was born in the 19th century CE.
- Years before India’s Independence: India gained independence in 1947 CE. To calculate the number of years before Independence:
1947 CE − 1828 CE = 119 years before India’s Independence
(d) Turn ‘12,000 years ago’ into a date.
Answer:
2024 CE − 12,000 years = 9976 BCE
So, “12,000 years ago” corresponds to approximately 9976 BCE.
Question 4. Plan a visit to a nearby museum: the visit should be prepared with some prior research on the kind of exhibits the museum holds. Keep notes during the visit. Write a brief report afterwards, highlighting what was unexpected / interesting / fun about the visit and the exhibits.
Answer: Before visiting a museum, research the types of exhibits it has, such as historical artifacts, paintings, or sculptures. During the visit, take notes on the displays, especially anything that stands out or surprises you. Afterward, write a brief report describing what you found interesting, any unexpected discoveries, and what aspects of the visit you enjoyed the most.
Question 5. Invite to your school an archaeologist or a historian and ask them to speak on the history of your region and why it’s important to know it.
Answer: Arrange for an archaeologist or historian to visit your school and give a talk on the history of your region. They can explain the significance of local historical events and why it’s important for students to understand their region’s past. This can help foster a deeper connection to the community and an appreciation for historical knowledge.
The Big Questions (Page 59)
Question 1. How do we measure historical time?
Answer: Historical time is measured using calendars and timelines. Different cultures have their own methods, such as the Gregorian calendar, which is widely used today, alongside others like the Hindu, Muslim, and Chinese calendars. Time is often divided into eras, centuries, and millennia, marked by significant events, such as the birth of Jesus Christ, which serves as a reference point for the Common Era (CE) and Before Common Era (BCE).
Question 2. How can various sources help us understand history?
Answer: Various sources, including documents, artifacts, fossils, inscriptions, and oral traditions, help us understand history by providing evidence of past events and cultures. Historians analyze these sources to reconstruct and interpret historical events. Different sources can confirm or sometimes contradict each other, allowing historians to piece together a more accurate picture of the past.
Question 3. How did early humans live?
Answer: Early humans lived in groups, primarily as hunters and gatherers, relying on hunting animals and collecting edible plants for survival. They sought shelter in caves or rock shelters and developed tools and weapons made of stone. They communicated through simple languages and created art, as seen in ancient rock paintings. Over time, they began to domesticate animals, cultivate crops, and form settled communities near rivers, leading to more complex social structures.

No. 1 study website