Solutions For All Chapters – Social Science Class 7
The Constitution of India — An Introduction
1. “The Constituent Assembly had representatives from diverse backgrounds in India.” Why do you think it was important to have a diverse set of representatives from all over India?
Answer:
It was important to have diverse representatives in the Constituent Assembly because India is a large country with many different cultures, languages, religions, and regions. Including people from all these backgrounds ensured that the Constitution would reflect the needs and views of everyone. This diversity helped make fair rules that work for all Indians, promoting unity and equality.
2. Read the statements below carefully and identify which key features/values in the Constitution of India are reflected in each statement.
a. Sheena, Rajat, and Harsh are standing in a line. They are excited to cast their first vote in the general elections.
Answer:
This reflects the value of Democracy and the Right to Vote. The Constitution ensures that every adult citizen has the right to vote and choose their leaders.
b. Radha, Imon, and Harpreet study in the same class in the same school.
Answer:
This reflects the value of Equality and the Right to Education. The Constitution ensures that all children, regardless of their background, have equal access to education.
c. Parents must make arrangements to ensure their children’s education.
Answer:
This reflects the Fundamental Duty of parents to provide education to their children between the ages of 6 and 14, as mentioned in the Constitution.
d. People of all castes, genders, and religions can use the village well.
Answer:
This reflects the value of Equality and Justice. The Constitution ensures that no one is discriminated against based on caste, gender, or religion and promotes equal access to public resources.
3. It is said that ‘All citizens in India are equal before the law’. Do you think this is a fact? If yes, why? If not, why not? Formulate your arguments.
Answer:
Yes, it is a fact that all citizens in India are equal before the law, as stated in Article 14 of the Constitution. This means everyone, no matter their caste, religion, gender, or status, is treated the same by the law. For example, if someone breaks a law, they face the same punishment regardless of who they are. However, in some cases, this may not feel true because of social inequalities, like poverty or discrimination in society. While the law ensures equality, we need to work together to make sure society follows this principle fully.
4. You have learnt that ‘India is the only country that provided universal adult franchise to its citizens from the beginning.’ Can you explain why India did it?
Answer:
India provided universal adult franchise (the right for every adult to vote) from the beginning because the leaders of the freedom struggle believed in equality and democracy. They wanted every Indian, regardless of caste, gender, or education, to have a say in choosing the government. This was important to unite the diverse country and ensure that all citizens could participate in building a new, free India.
5. How did the freedom struggle inspire the making of the Constitution of India? How did India’s civilisational heritage inspire some of the key features in the Constitution of India? Explain.
Answer:
- Freedom Struggle: The Indian freedom struggle inspired the Constitution by promoting values like equality, justice, freedom, and fraternity. Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar fought for these ideals, which were included in the Constitution. For example, the struggle for independence showed the importance of giving everyone the right to vote and ensuring fairness in society.
- Civilisational Heritage: India’s ancient culture and history also shaped the Constitution. Ideas like vasudhaiva kutumbakam (the world is one family) and respect for nature and diversity were included. For example, the Fundamental Duties, such as protecting the environment and preserving cultural heritage, reflect India’s traditional values of living in harmony with nature and respecting all people.
6. Do you think we, as a society, have achieved all the ideals of the Constitution? If not, what can we each do as citizens to move our country closer to these ideals?
Answer:
No, we have not fully achieved all the ideals of the Constitution, such as complete equality and justice for all. For example, some people still face discrimination based on caste, gender, or religion, and poverty prevents equal opportunities. As citizens, we can:
- Treat everyone with respect and fairness.
- Follow the Fundamental Duties, like protecting the environment and promoting unity.
- Educate others about their rights and duties.
- Support laws and policies that promote equality and justice.
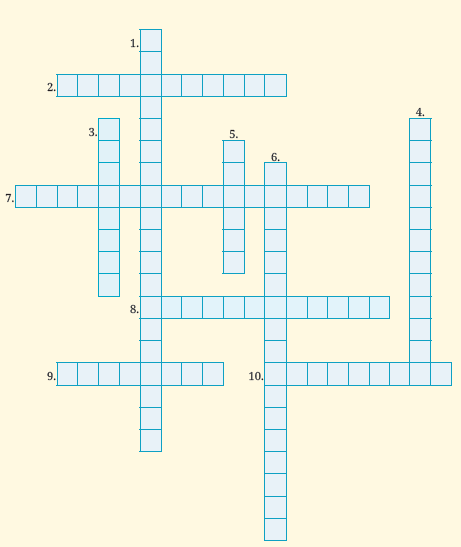
7. Read the clues carefully to solve the crossword on the next page to uncover important concepts from the Indian Constitution.
Across
2. The branch of government that makes laws.
7. The part of the Constitution that outlines the duties of citizens towards the country.
8. The highest court in India that protects the Constitution.
9. A system where the head of state is elected, not hereditary.
10. The process by which the Constitution can be changed over time.
Down
1. The group of people who wrote the Indian Constitution.
3. The statement at the beginning of the Constitution that tells us the values it upholds.
4. The document that lays out the rules and laws of a country.
5. The gas used to preserve the original Constitution safely.
6. Basic rights given to every citizen, like freedom and equality
Answer :
Across
2. LEGISLATURE: The branch of government that makes laws.
3. FUNDAMENTALDUTIES: The part of the Constitution that outlines the duties of citizens towards the country.
4. SUPREMECOURT: The highest court in India that protects the Constitution.
5. REPUBLIC: A system where the head of state is elected, not hereditary.
6. AMENDMENT: The process by which the Constitution can be changed over time.
Down
1. CONSTITUENTASSEMBLY: The group of people who wrote the Indian Constitution.
2. PREAMBLE: The statement at the beginning of the Constitution that tells us the values it upholds.
3. CONSTITUTION: The document that lays out the rules and laws of a country.
4. HELIUM: The gas used to preserve the original Constitution safely.
5. FUNDAMENTALRIGHTS: Basic rights given to every citizen, like freedom and equality.
Key to read the filled grid attempt:
Each word starts at its numbered position.
1D: CONSTITUENTASSEMBLY
2A: LEGISLATURE
3D: PREAMBLE
4D: CONSTITUTION (appears on the far right, vertically)
5D: HELIUM
6D: FUNDAMENTALRIGHTS
7A: FUNDAMENTALDUTIES
8A: SUPREMECOURT
9A: REPUBLIC
10A: AMENDMENT
The Big Questions (Page 209)
1. What is a constitution, and why do we need one?
Answer:
A constitution is a document that contains the basic rules and laws of a country. It explains how the government should work, what rights and duties citizens have, and the goals of the nation. For example, it tells us how laws are made, who can vote, and how the government is divided into the legislature, executive, and judiciary .
We need a constitution because it acts like a rulebook for the country. Just like a kabaddi game needs rules to avoid fights, a country needs a constitution to ensure fairness, solve disputes, and protect everyone’s rights. It helps the government work properly and ensures that all citizens are treated equally.
2. How was the Indian Constitution prepared?
Answer:
The Indian Constitution was prepared by a group called the Constituent Assembly. This group had 389 members at first (later reduced to 299 after Partition), including 15 women, who came from different regions and backgrounds in India. They started working on 9 December 1946. Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the Chairman, and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar led the Drafting Committee, which wrote the initial text.
The Assembly took almost three years to finish the Constitution. They discussed many ideas and completed the document on 26 November 1949. It came into effect on 26 January 1950, which is why we celebrate Republic Day on that date.
3. How did our freedom struggle and civilisational heritage influence the Constitution?
Answer:
- Freedom Struggle: The Indian freedom struggle inspired the Constitution by giving it values like equality, justice, freedom, and fraternity. Many leaders of the freedom movement were in the Constituent Assembly, and they wanted these values to be part of the Constitution. For example, the struggle showed the importance of giving everyone the right to vote and ensuring fairness for all.
- Civilisational Heritage: India’s ancient culture and history also shaped the Constitution. Ideas like vasudhaiva kutumbakam (the world is one family) and respect for nature and diversity were included. For example, the Fundamental Duties, such as protecting the environment and preserving cultural heritage, come from India’s traditions. The Constitution also reflects the idea of accepting different viewpoints, which is part of India’s history.
4. What are the key features of the Constitution of India? Why is it still relevant, even though it was written more than seventy years ago?
Answer:
Key Features of the Constitution:
It defines the three organs of government: the legislature (makes laws), executive (implements laws), and judiciary (ensures laws are followed), with a separation of powers.
It has a three-tier system: central, state, and local (Panchayati Raj) governments.
It includes Fundamental Rights, like the right to equality and freedom.
It lists Fundamental Duties, like respecting the National Flag and protecting the environment.
It has Directive Principles of State Policy, which are goals for the government, like ensuring a good standard of living for all.
The Preamble lists values like justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Why It Is Still Relevant:
The Constitution is still relevant because it is a living document that can be changed through amendments to meet new needs, like adding Fundamental Duties in 1976 or the Panchayati Raj system in 1992. It protects the rights of all citizens and promotes equality, which are important even today. Its values, like justice and fraternity, help India stay united despite its diversity, making it useful even after more than seventy years.

Leave a Reply